
Hepatitis-Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options

Table of Contents
Introduction
Hello everyone,
On Saturday 9th July 2022, one patient visited my clinic with complaints of nausea, pain in abdomen, mild fever and loss of appetite. On clinical examination, abdominal palpitation revealed a slightly swollen liver. This prompted me to ask him ” How is your urine color?” The reply was prompt-” Dark yellow”. I immediately suspected Infective Hepatitis.
This made me prescribe him some investigations [as shown below]. Well, I was correct- the investigation reports revealed that he is indeed suffering from infective hepatitis.
Monsoon is one season that if care is not taken, one can be a victim to many illnesses. I have written a few articles earlier on some monsoon diseases, which you can look into at the end of this article.
What is Hepatitis?
Hepatitis is a disease that affects the liver. The word “hepatic” means “related to the liver.” Hepatitis can be acute (short-term) and chronic (long-term) in nature. Acute hepatitis is an infection of the liver, which resolves on its own within six months in most people. Read on to know more about Hepatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options.
Why am I writing about Hepatitis?
In the preceding 2 years, the Covid-19 had prevented people from venturing out as well as eating out because eateries all over the world were practically closed. Now that the lockdown has been lifted, the open-air vendors are back on the street. They are not very hygienic in their approach to selling food. Moreover, the monsoon season has begun in India and with that, common houseflies are hovering over the open-source foods. These houseflies are carriers of diseases like typhoid and hepatitis.
In the past, I have authored an article on several types of infective and contagious diseases. In line with the diseases mentioned in that article, and because monsoon is going on in India, viral hepatitis affects most people eating from unhygienic vendors.
What happens in Hepatitis?
As mentioned earlier, hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. It is a common condition that can range from mild to serious. There are many different causes of hepatitis. Some are acute (short-term) and some are chronic (long-term).
Acute hepatitis is an infection of the liver, whereas chronic hepatitis is not an infection. In acute hepatitis, symptoms can range from mild to severe and may last a few weeks to months.
In chronic hepatitis, symptoms are often mild but can last for years. Hepatitis can be caused by viruses, drugs, or alcohol. Viral hepatitis is by far the most common type of hepatitis and is transmitted through contact with infected blood or other bodily fluids.
Viral hepatitis can be either acute or chronic, and it can be either mild or serious. There are six major types of viral hepatitis: Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E, and G.
Types of Hepatitis
Hepatitis can be acute or chronic.
- Acute hepatitis is an infection of the liver and is caused by an infection from one of many different hepatitis viruses. which resolves on its own within 6 months in most people. It is usually short-term (can last up to 6 months) and resolves on its own. Acute hepatitis is usually mild, but sometimes it can be serious.
- Chronic hepatitis is not an infection of the liver in a real sense. It occurs when the liver is injured, often from long-term use of certain medications or alcohol or due to high cholesterol level [NALD]. In chronic hepatitis, symptoms are often mild but can last for years.
Symptoms of Hepatitis
Acute hepatitis –
Symptoms of acute hepatitis can range from mild to severe. Symptoms may last a few weeks to months. Common symptoms include: –
- Swollen or tender liver (hepatomegaly) – This is the most common symptom.
- Fever – This happens in about 25% of people with acute hepatitis.
- Loss of appetite – This is seen in about 70% of people with acute hepatitis.
- Nausea – This is a prominent symptom.
- Abdominal pain – This is seen in about 50% of people with acute hepatitis.
- Jaundice – This is the yellowing of the skin and eyes that happens when the liver does not break down old red blood cells properly.
- Dark yellow urine
Chronic hepatitis –
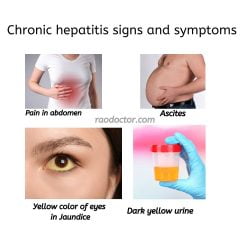
Symptoms of chronic hepatitis are often mild but can last for years.
Common symptoms include: –
- Fatigue – Loss of appetite and weight loss.
- Swollen or tender liver.
- Chronic pain in the abdomen.
- Nausea or vomiting occasionally.
- Chronic Jaundice.
- Ascites- this is accumulation of fluid in the abdomen causing severe distension. It is a sign of liver failure
- Liver cancer- this can be a feature of hepatitis B.
What are the tests recommended for diagnosing hepatitis?
Blood Tests – During a medical assessment, the doctor will do a blood test to check your liver function. This test gives information about your liver’s ability to break down proteins and process insulin, which is important for your blood sugar levels.
I usually recommend the following tests to diagnose/rule out hepatitis-
- Complete blood checkup.
- Liver function test- this includes blood levels of
- bile pigments called bilirubin, Bilirubin is a byproduct of destruction of red blood cells in the blood. This is mostly increased in Acute Infective Hepatitis.
- liver enzymes, like SGOT, SGPT, Alkaline phosphatase
- HbsAg- this is also called the Australia antigen Test. This test is used to detect Hepatitis B.
As mentioned above, one patient visited me with complaints of nausea, vomiting and mild fever. On clinical examination, I found his liver to be slightly enlarged. Here is a sample of the test reports that I recommended-
Liver Function Test or LFT

Urine Routine and Microscopic
His urine report also revealed presence of Bile pigments that are a hallmark of infective hepatitis and that which gives a dark yellow hue to the urine sample.

This patient has since been admitted to the hospital for further treatment and will remain there till he recovers fully. In the hospital, they diagnosed him to be suffering from Hepatitis A infection.
Hepatitis B and C Tests – If your doctor suspects that you have hepatitis B or C, you may need to take a blood test for these viruses. These are Elisa [enzyme linked immunoassay] like HbsAg.
Other Tests – If your doctor suspects that you have an infection in your liver, like amoebic hepatitis, you may need to have an imaging test, such as an ultrasound or computed tomography (CT) scan.
Causes of Hepatitis
There are several types of hepatitis viruses that give rise to either acute or chronic disease. Other than viral cause, the other causes are-
- Alcoholic hepatitis- caused due to excessive alcohol consumption
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [NAFLD]- caused due to excess deposition of cholesterol or fats in the liver, also known as fatty liver disease.
People can get hepatitis from contact with infected blood or other bodily fluids. Viral hepatitis is by far the most common type of hepatitis and is transmitted through contact with infected blood or other bodily fluids. Viral hepatitis can be either acute or chronic, and it can be either mild or serious.
There are six major types of viral hepatitis: Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E, and G. Let’s study them one by one-
- Hepatitis A – Hepatitis A is usually caused by eating food that contains the virus. It can also be transmitted through saliva or mucus by close contact with an infected person. It is a common illness associated with travel to areas with poor sanitation or hygiene.
- Hepatitis B – Hepatitis B is most often spread through the bloodstream by contact with infected blood. Infection usually occurs when blood from an infected person gets into the bloodstream of another person.
- Hepatitis C – Hepatitis C is a blood-borne virus that can be spread through blood, blood-to-blood contact (for example, through needle sharing or medical procedures), or sexual contact with an infected person.
- Hepatitis D – Hepatitis D is caused by a virus that is very similar to the hepatitis B virus. It is a rare type of hepatitis that is acquired in the same way as hepatitis B and C.
- Hepatitis E – This type of hepatitis is caused by a virus that is found in feces. It is spread when an infected person does not wash their hands after going to the bathroom and then touches food or water. Hepatitis E can also be contracted from eating food that has been contaminated by feces.
- Hepatitis G – This type of hepatitis is caused by a virus found in blood or blood products. It can also be passed from mother to child.
Treatment for Hepatitis
There is no specific treatment for acute hepatitis, as it resolves on its own in about 80% of people. The best treatment for acute hepatitis is to rest and to drink plenty of fluids. There is no specific treatment for chronic hepatitis, as it is a long-term condition. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, such as fatigue, weight loss, and loss of appetite.
Is hepatitis curable?
Avoiding some foods is the first step towards treatment of acute hepatis. I suggest patients should avoid fatty foods and have fresh fruits, fruit juices and sugary or starchy food like rice instead.
There is no specific cure for hepatitis. Liver has the capability of regenerating new cells and replacing the injured ones. The majority of people recover from the acute form of hepatitis within six months, so treatment is focused on relieving symptoms.
In India, herbal medicines are prescribed like Liv 52, Livomyn etc., by some doctors trained in Ayurveda.
People who have chronic hepatitis are advised to avoid risk factors such as alcohol, drugs, or certain medications that can damage the liver.
Are there any ways to prevent hepatitis other than personal hygiene?
The best way to prevent getting the disease is to avoid foods sold openly by street vendors, especially during monsoons.

Yes, there are vaccines to prevent hepatitis. You can get vaccinated for almost all the types of hepatitis. Here is a list of hepatitis vaccines that you can ask your doctor for-
- Hepatitis A vaccine- brand name- Biovac A vaccine
- Hepatitis B vaccine-brand names- GeneVac B adult and pediatric vaccine.
Currently there are no vaccines available for Hepatitis C, E, and G. However, the vaccine used for Hepatitis B is equally effective in preventing hepatitis D variety.
These vaccines are available at any pharmacy stores. You can also get them[or any other medicines] in India at a discounted rate online after uploading the doctor’s prescription by visiting these links
What are the complications of Hepatitis?
Patients suffering from fulminant disease, meaning where the liver has extensive damage such as very high enzyme values, [like the one shown in above investigations], can go into complications. This can be-
- Severe dehydration due to excessive vomiting.
- Disorientation and delirium due to infection reaching the brain, termed hepatic encephalopathy.
- Hepatic coma– Here the brain is so much affected that the patient becomes totally unconscious and goes into a condition called Coma.
When should a hepatitis patient be admitted to hospital?
As such, there is no need to admit a patient in the initial stages of the illness. Unless of course, if there are complications as described above.
- Acute hepatitis – People who have acute hepatitis that is severe or lasts longer than 6 months are admitted to the hospital. Acute hepatitis that is milder and which resolves in 6 months does not require hospitalization.
- Chronic hepatitis – People with chronic hepatitis are admitted to the hospital if their condition worsens, such as if they become jaundiced or have symptoms, such as fatigue, weight loss, or loss of appetite.
Prognosis for People with Hepatitis
Most people recover from acute hepatitis within 6 months, although some may take longer. Complications are rare. Most people with chronic hepatitis recover, but the condition may last for years. Complications are rare.
Conclusion
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. It can be caused by a virus, a drug, or alcohol. The best treatment for acute hepatitis is rest and to drink plenty of fluids. There is no specific treatment for chronic hepatitis, as it is a long-term condition. The prognosis for people with hepatitis is good, and most people recover with treatment.
Some useful links-
Fo a detailed study on hepatitis, click the links given below-
Here are some of the other monsoon diseases that you may like to know-
Hope this article has been useful to you. If you would like to get more articles like this in your mailbox, do fill in the subscription form that you see below-
