Table of Contents
Pneumonia- what is it, it’s signs and symptoms, complications, treatment and prevention
Our lungs can be subject to various ailments. One of them is pneumonia. This disease is common in places where there is either extreme humidity or cold climate.
It is also common in people who have low immunity like those suffering from HIV, cancer, diabetes and heart disease. All said, this disease can cause severe illness that lands most of the patients in hospital. So, I guess, that it is quite important that we learn about it.
Pneumonia is not a disease to be taken lightly. It can be life-threatening and requires urgent medical attention in order to prevent complications and shorten its duration.
If you are prone to getting sick often or have a weakened immune system, you should know how to prevent pneumonia and stay healthy, so you don’t get it again.
In the past, I have already discussed asthma and recently, lung cancer.
In this blog post, we will discuss the causes of pneumonia, its types, risk factors, complications, prevention tips, home remedies, and when to see a doctor.
What is pneumonia?
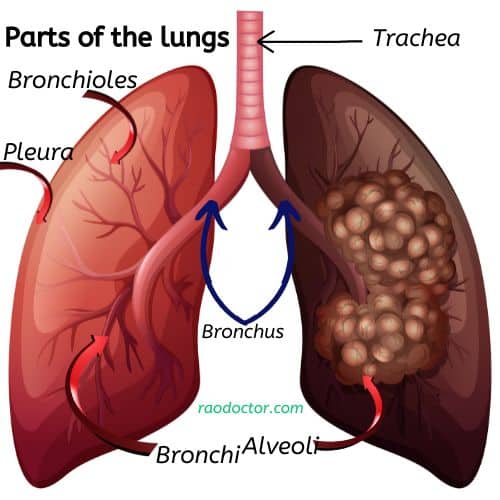
Before we start, let’s learn a bit about various parts of our lungs, because they are equally affected whenever some suffers from this disease.
Our lungs are made up of structures that help us breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. The various structures that make up our lungs is shown below:

Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs. It can be bacterial, viral, or fungal in nature and can affect people of all ages and genders.
Pneumonia can be life-threatening especially if you are at risk of complications. It is, therefore, necessary to prevent pneumonia and stay healthy so you do not get it again.
The infection most commonly occurs when bacteria or virus gets into the lungs through the airways and begins to multiply, leading to inflammation. Rarely, spores of fungus from molds in the house walls or hay barns on farms can cause a dangerous form of pneumonia called aspergillosis.
Sometimes, the lungs may get infected without any apparent cause. The infection can get worse if not treated on time, leading to complications such as lung failure.
Know the causes of pneumonia
There are many causes of pneumonia. Let’s discuss the most common causes of pneumonia.
- Viral infection – Viral infections like the common cold and influenza are the most common cause of pneumonia. Viral infections can cause the lining of our airways to become inflamed.
- According to cdc.gov, common causes of viral pneumonia are influenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19).
- Bacterial infection – Bacterial infections are another common cause of pneumonia. Bacteria can enter the lungs through the airways, blood, or from the skin.
- Common causes of bacterial pneumonia are Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) and Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
- Anatomical abnormalities – People with anatomical abnormalities like cystic fibrosis are at high risk of developing pneumonia. Other anatomical abnormalities that can lead to pneumonia are :
- bronchiectasis,
- lung cancer, and
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease).
- Poor immune system – People with poor immune systems are at risk of developing pneumonia. Those with weakened immune systems like people suffering from HIV infection or people undergoing chemotherapy or radiation treatments are at risk of developing pneumonia.
- Respiratory tract infections – Respiratory tract infections like
- sinusitis,
- laryngitis, and
- bronchitis can increase your risk of developing pneumonia.
- Lack of vitamin D – Studies show that people with low levels of vitamin D are at risk of developing pneumonia.
- Fungal infection – Aspergillosis is a rare yet dangerous form of pneumonia experienced by people working on farms. The causative organism is spores of mold fungi called aspergillus.
Useful Article: Causes of Pneumonia
What are the signs and symptoms of pneumonia?
The signs and symptoms of pneumonia depend on the type of pneumonia you have: –
- Viral pneumonia – Viral infections may not cause any symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they may include
- a cough,
- runny nose,
- sneezing,
- fever, and
- general feelings of unwellness or sickness.
- Bacterial pneumonia – People with bacterial infections may experience symptoms like
- a cough that brings up green or yellow sputum,
- general feelings of unwellness,
- high fever, and
- shivering.
- Tuberculosis (TB) – TB is a bacterial infection due to mycobacterium tuberculosis that can cause a cough that brings up blood. It usually causes symptoms after 3 to 9 months after its initial infection.
- Pneumonia in children – Children with pneumonia may experience
- fever,
- fatigue,
- irritability,
- poor feeding, and
- poor weight gain.
What are the investigations in pneumonia
Certain investigations can help diagnose pneumonia. These include: –
- Blood test – A blood test can show signs of infection or inflammation in the lungs. Complete Blood Count [CBC], blood culture, blood gases (in hospitalized cases) are some of the common investigations that may be ordered by your doctor. CBC may show a high white blood cell count with predominance of neutrophils, a white blood cell that has protective properties.
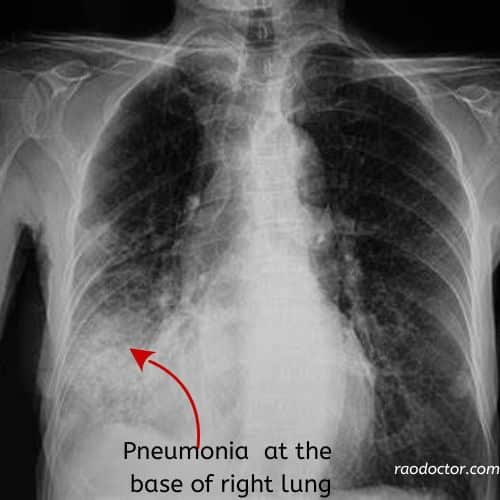
- X-ray – An X-ray can help visualize the lungs, bones, and chest. The X-ray picture below shows how pneumonia appears in the lungs.
- CT scan – A CT scan can help visualize the lungs, blood vessels, and liver. In the recent Covid-19 pandemic, HRCT imaging was frequently used to diagnose Covid pneumonia.
- Sputum culture – A sputum culture can help identify bacterial infections that cause pneumonia.
What are the risk factors for pneumonia?
Knowing about risk factors that cause pneumonia is helpful in preventing it. These are the commonly encountered risk factors:
- Poor immune system – People with weakened immune systems are at high risk of developing pneumonia. Such people include those
- with autoimmune disorders such as HIV infection,
- cancer,
- heart failure, or
- diabetes.
- Smoking – Smoking damages the lungs and makes them more susceptible to bacterial infections.
- Alcohol abuse – Frequent alcohol abuse damages the immune system and makes it harder for your body to fight infections.
- Asthma – People with asthma are at risk of developing bacterial infections. –
- Cystic fibrosis – People with cystic fibrosis of the lungs are at high risk of developing bacterial infections.
- Respiratory tract infections – People with repeated or persistent or poorly treated respiratory tract infections are at risk of developing bacterial lung infections.
- Pneumonia in children – Children are at risk of developing pneumonia because their immune systems are not fully developed.
What are the complications of pneumonia?
Some possible complications of pneumonia include:
Lung abscesses
These are pus-filled cavities in the lung that can cause fever, cough, chest pain and bad breath.
Pleural effusion
This is a buildup of fluid between the layers of tissue that line the lungs and chest cavity. This can cause chest pain, shortness of breath and reduced lung function.
Empyema
This is a collection of pus in the pleural space that can cause fever, chills, chest pain and breathing difficulties.
Sepsis or bacteremia
This is a serious condition that occurs when the infection spreads to the bloodstream and causes inflammation throughout the body. This can lead to organ failure, shock and death.
Respiratory failure
This is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the lungs cannot provide enough oxygen to the body or remove enough carbon dioxide from the blood. This can cause confusion, drowsiness, rapid breathing and bluish skin.
The most common complication of pneumonia depends on the type and severity of the infection, as well as the age and health status of the person.
These complications can be serious and require medical attention. If you have any questions about pneumonia, you may please put them in the comment box. I will respond to them promptly.
When to see a doctor for pneumonia?
You should see your doctor if you experience these signs and symptoms-
- Moderate to high fever for more than 3 days – Fever is a sign of inflammation in the body. If your fever does not go down for 3 days, consult a doctor.
- Cough – If your cough does not go away in 10 days, see a doctor.
- Shortness of breath – If you experience shortness of breath even while resting, it can be a sign of pneumonia.
- Strength reduction – If you feel weaker than usual, it can be a sign of bacterial infections of the lungs.
- Chest pains – Chest pains are a sign that your lungs parts like the pleura are inflamed.
- Headache – Sometimes, persistent headache with fever is a sign of bacterial infection.
Tips to prevent pneumonia.
Keep your immune system strong
This can be done by eating healthy foods, drinking lots of water, and exercising regularly. Avoid overeating foods that are known to weaken the immune system such as caffeine and alcohol.
Washing hands
Wash your hands regularly with soap and water. This is the best way to kill germs and avoid getting sick.
Get vaccinated
Vaccines help prevent infections by boosting your immune system. –
Avoid these
- Avoid close contact with people who are sick.
- Avoid visiting places with poor ventilation.
Home remedies to prevent pneumonia
Eat a healthy diet – A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals will help boost your immune system and keep you fit.
Take vitamin C – Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that boosts the immune system. –
Include garlic in your diet – Garlic is known to boost the immune system. –
Breathe in the scent of eucalyptus – Eucalyptus is known to boost the immunity system. –
Get enough sleep – Sleep is very important in boosting your immune system and keeping you fit. –
Exercise – Regular exercise will help improve your immune system and keep you fit. –
Take probiotics regularly – Probiotics are known to boost the immune system and are found in fermented foods and supplements. A natural way to get probiotics is having yogurt or curd in your diet. Nowadays, probiotic supplements are freely available, sometimes combined with antibiotics prescribed by your doctor.
Treatment of Pneumonia
Whenever your doctor makes a diagnosis of pneumonia, depending upon the severity, he/she may prescribe medicines like antibiotics, cough expectorants, medications for fever and body pain, etc.; or he may suggest you get admitted in hospital as there is a likelihood of you having low oxygen levels in your blood.
However, I suggest that your doctor suggest the line of management best for you.
Conclusion
Preventing pneumonia is crucial as it can be deadly if not treated properly. It is important to follow the above tips and keep your immune system strong so that you do not contract viral or bacterial infections. If you do get sick, follow the above tips and see a doctor to get treated.
Useful Articles:
- Mayo Clinic on Pneumonia
- CDC on pneumococcal disease
- VeryWell Health on Viral vs Bacterial pnuemonia
Final words
I hope you have understood all about pneumonia in this article. If you have found it useful, do share with your family members and friends through the social media icons at the bottom of this article. Alternately, you can Click to Tweet if you have a Twitter account-
How to Prevent Pneumonia and Stay Healthy: 9 Tips for you Share on XMy next article will be on some common blood tests that are regularly ordered by your doctor to understand and treat your ailment or disease.