Learn all about various fungal skin infections
Table of Contents
What are fungal skin infections?
Fungal skin infections are caused by a variety of fungi, which can result in a wide range of symptoms and signs, depending on the type of infection. Unlike Psoriasis, about which I wrote in my previous article, fungal skin infections can affect anyone. If have not read that article yet, you can find it here-
The most common types of fungal skin infections include:
- Athlete’s foot, also called Tinea Pedis
- Ringworm, also called Tinea Corporis
- Jock itch, also called Tinea Cruris and
- Yeast infections, also called Candidiasis.
It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of a fungal skin infection so that it can be treated promptly and effectively.
If you are not keen on reading, you can listen [and scroll down while listening] to this article here-
Athlete’s foot is a fungal skin infection of the feet and toes, caused by the fungus Trichophyton rubrum. It is characterized by itching, burning, and cracked, peeling skin. Other common signs of athlete’s foot include redness, swelling, and blisters. Patients of diabetes are more prone to this infection.
Ringworm is another common type of fungal skin infection, which is characterized by an itchy, scaly, red rash that is usually circular in shape. It is caused by various fungi, including Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, and Microsporum.
Jock itch is a fungal skin infection that affects the groin area and is caused by the same fungus that causes athlete’s foot. It is characterized by an itchy, red rash that is usually found on the inner thighs, buttocks, and genital area.
Yeast infections are a type of fungal skin infection caused by the fungus Candida albicans. They are characterized by itching, burning, and redness of the skin, as well as white patches that look like cottage cheese.
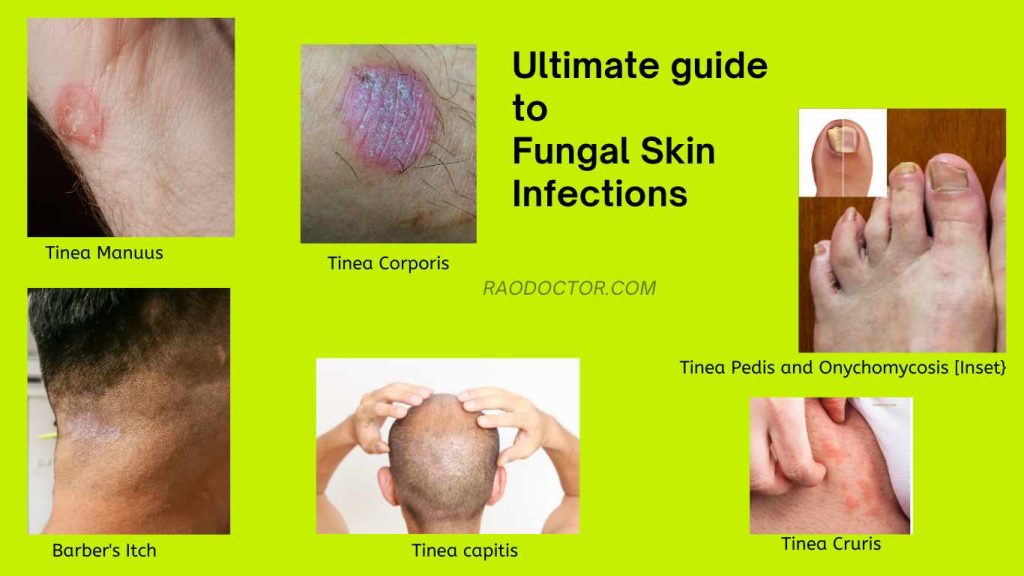
Different types of fungal skin infections according to locations on the body-
Depending on the area they affect, fungal infections have different names.
Below are the types and names of fungal skin infections area wise:

Feet:
- Athlete’s foot (tinea pedis)
- Toe web infection (interdigital tinea pedis/candidiasis)
- Foot ringworm (tinea corporis)
- Nail fungus (onychomycosis)
Groin:
- Jock itch (tinea cruris)
Scalp and hair:
- Ringworm of scalp (tinea capitis), also called Barber’s Itch [ see the cover picture]
- Ringworm of the beard (tinea barbae)
Body:
- Ringworm of the body (tinea corporis)
Hands:
- Fungal nail infections (onychomycosis)
- Hand fungus (tinea manuum)
Face:
- Facial ringworm (tinea faciei)
All these presentations are shown in the cover picture, right below the heading.
Some of these fungal infections can affect multiple areas alone. For example, tinea corporis can affect the scalp, face, and body.
Here are some examples of commonly occurring fungal skin infections-
- Athlete’s foot is a common fungal skin infection affecting the feet. It causes itching, redness, and burning between the toes and the soles of the feet.
- Jock itch is a fungal infection that affects the groin area, causing itching, burning, and redness in the affected area.
- Ringworm of the scalp is a common fungal infection affecting the scalp and hair, especially in children. It causes intense itching and loss of hair.

The treatment for fungal skin infections
This depends on the type of infection. Generally, antifungal creams and ointments are used to treat athlete’s foot, ringworm, and jock itch.
For yeast infections, antifungal creams and oral medications may be prescribed. It is important to follow the doctor’s instructions closely and continue treatment for the recommended length of time in order to ensure that the infection does not return.
Medicines used in treatment of Fungal Skin Infections
Antifungal drugs are used in the treatment of fungal skin infections
The dosage and duration of therapy depend on the type and severity of the infection
Some commonly used antifungal drugs and their daily dosages for treating fungal skin infections include:
- Clotrimazole (1% cream) – Apply twice daily to the affected area. Clotrimazole is also available in powder form that you can put on affected areas after bath. Speaking of baths, kindly do not use normal body soap to clean your affected areas- soap aggravates this disease. Instead, use a medicated soap [mentioned below]. E.g. Candid cream.
- Miconazole cream- very effective in getting rid of jock itch. Available in combination with steroid cream too. Eg. ZOLE, ZOLE- F OINTMENTS.
- Terbinafine (1% cream) – Apply once or twice daily for up to 4 weeks
- Ketoconazole (2% cream) – Apply once or twice daily for up to 4 weeks. This is also available in shampoo form for treating Tinea capitis or scalp ringworm. Eg. Keto shampoo.
- Luliconazole cream, spray, lotion is a very good option to speed up recovery. Sprays and lotions are very effective in treating nail fungal infection (Onychomycosis). E.g. Lulimax cream, L-Sys spray or lotion
- Fluconazole (150 mg tablet) – Take one tablet orally once a week for up to 6 weeks. For onychomycosis of fingers, once weekly for 6 months and for toenail infection, once weekly for 12 months. E.g.- Flucos 150 tablet.
- Itraconazole (100-200 mg capsule) – Take once or twice daily for 1-4 weeks. E.g. Itrasys 100/ Itrasys 200 tablets.
- Griseofulvin tablets (250 t0 500mg) were commonly prescribed in the past for 2 to 3 weeks. E.g. Grisovin 250 tablets.
- Ketoconazole soap, to be used while having bath, is also prescribed to speed up recovery. Eg. Keto soap, Ketomed soap.
It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and duration of therapy to ensure complete clearance of the infection and prevent relapse.
Depending on the severity and location of the infection, some antifungal drugs may also be prescribed in a topical or oral form. For example, severe or widespread infections may require oral antifungal medications such as fluconazole or itraconazole.
What other precautions should you take to prevent this disease?
In addition to medical treatment, there are some simple steps that can be taken to prevent and treat fungal skin infections.
These include keeping the skin clean and dry, avoiding tight-fitting clothing, and wearing cotton socks and breathable shoes.
Additionally, it is important to avoid sharing towels and other personal items, as this can spread the infection.
Conclusion
Fungal skin infections are very common in places where the humidity is more and sweating is excessive, so much so that your undergarments get soaked.
Moreover, in places where the rainfall is heavy and clothes take time to dry, using half dry undergarments causes tinea cruris and tinea corporis.
All said and done, this skin infection is treatable, and it can be treated effectively.
Useful resource- Fungal skin infections
Final words
I hope this article has explained to you all about fungal skin infections. I would be highly obliged if you could share this article with your family and friends on social media by clicking on the icons at the bottom of this article. If you have a Twitter account, do consider sharing there by using the link given below-
Ultimate Guide To Fungal Skin Infections-learn How to Tackle Them Share on XMy next article will be on an important brain disease called STROKE. Be sure to log into raodoctor.com and read that article as and when it is published. Alternately, you can sign up by joining my e-mail list and get notified about future articles.
Adios.