Table of Contents
Introduction
Statin therapy is commonly prescribed to patients with high cholesterol levels to help lower their risk of cardiovascular diseases.
While statins are generally safe and effective, there are potential side-effects that patients need to be aware of.
Potential side effects of statin use
Common side effects of using statins include muscle pain or weakness, liver damage, digestive issues, and increased blood sugar levels.
Some commonly used statins and their specific side effects are:
- Atorvastatin (Lipitor): Muscle pain, liver damage, digestive problems.
- Simvastatin (Zocor): Muscle pain, liver damage, digestive problems.
- Rosuvastatin (Crestor): Muscle pain, liver damage, digestive problems.
- Pravastatin (Pravachol): Muscle pain, liver damage, digestive problems.
- Lovastatin (Mevacor): Muscle pain, liver damage, digestive problems.
One of the most common side-effects of statin therapy is muscle pain or weakness. This can range from mild discomfort to severe muscle damage.
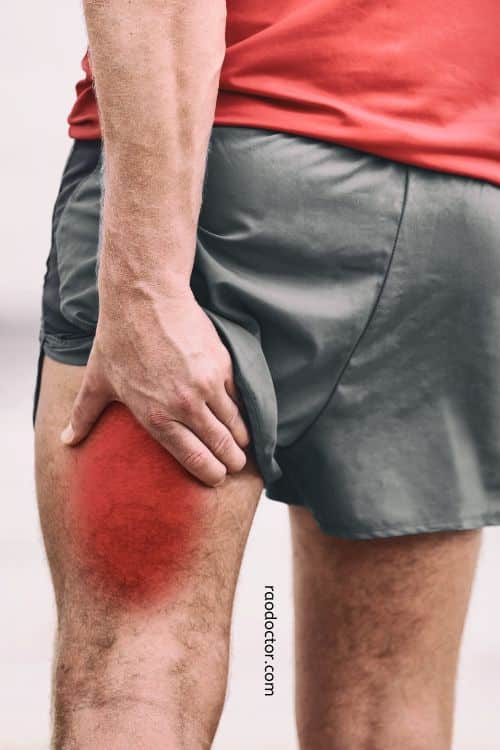
In rare cases, statins can lead to a condition called rhabdomyolysis, which is characterized by the breakdown of muscle tissue.
Rhabdomyolysis can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
Rhabdomyolysis can be life-threatening due to the risk of kidney damage and potential complications such as acute kidney injury and electrolyte imbalances.
It requires immediate medical attention to prevent further muscle breakdown, manage potential complications, and ensure proper treatment.
What precautions should you take while on Statins?
To minimize the risk of side-effects, it is important for patients to take certain precautions when undergoing statin therapy.
Firstly, it is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and not exceed the recommended amount. Taking higher doses of statins can increase the likelihood of experiencing side-effects.
Additionally, it is important to inform your healthcare provider about any other medications or supplements you are taking, as some drugs can interact with statins and increase the risk of side-effects.
Regular monitoring of liver function is also recommended, as statins can sometimes affect liver enzymes.
What is Rhabdomyolysis?
Now, let’s explore what rhabdomyolysis is. Rhabdomyolysis is a rare but serious condition that can occur as a result of statin therapy or other factors that cause muscle damage.
It is characterized by the breakdown of skeletal muscle tissue, which releases myoglobin and other toxic substances into the bloodstream. This can lead to kidney damage and other complications if not treated promptly.
The symptoms of rhabdomyolysis include
- severe muscle pain,
- weakness, and
- dark-colored urine or cola colored urine.
In some cases, individuals may also experience fever, nausea, and confusion.
If you experience any of these symptoms while taking statins, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Useful resource- Rhabdomyolysis
What to do if you feel that you have side-effects of statins?
Treatment for rhabdomyolysis typically involves stopping the use of statins and providing supportive care to prevent further muscle damage. This may include intravenous fluids to flush out the toxins and medications to protect the kidneys. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required.
What should I avoid when taking statins and why?
Avoid consuming grapefruit or grapefruit juice while taking statins because it can interfere with the effectiveness of the medication and increase the risk of side effects.
Other than grapefruit, there are some drugs that should be used with precaution when one is on statins. Some drugs that can interact with statins and cause side effects are:
- Gemfibrozil
- Cyclosporine
- Niacin
- Erythromycin
- Clarithromycin
- Verapamil
- Diltiazem
- Amiodarone
- Warfarin
- Protease inhibitors (HIV medications)
Please consult with your healthcare provider for specific information and guidance regarding drug interactions with statins.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while statin therapy is generally safe and effective in reducing cholesterol levels and preventing cardiovascular diseases, it is important for patients to be aware of the potential side-effects.
Muscle pain or weakness is a common side-effect, but rhabdomyolysis, although rare, can be a serious complication.
Taking precautions, such as following the prescribed dosage and regularly monitoring liver function, can help minimize the risk of side-effects.
If any symptoms of rhabdomyolysis occur, immediate medical attention should be sought to prevent further complications.
