What is heart arrhythmia
Heart arrhythmia refers to an irregular heartbeat, where the heart beats too fast, too slow, or in an abnormal rhythm.
This can occur due to various reasons such as age, heart disease, high blood pressure, and electrolyte imbalances.
Arrhythmias can be classified into different types based on their origin and impact on the heart’s function. Some common types include atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and sinus bradycardia.
These arrhythmias can be identified through an electrocardiogram (ECG), a diagnostic tool that records the electrical activity of the heart.

Atrial fibrillation (AF)
AF is one of the most common arrhythmias and occurs when the upper chambers of the heart (atria) beat irregularly and rapidly. This can lead to a decreased pumping function of the heart and an increased risk of blood clots.
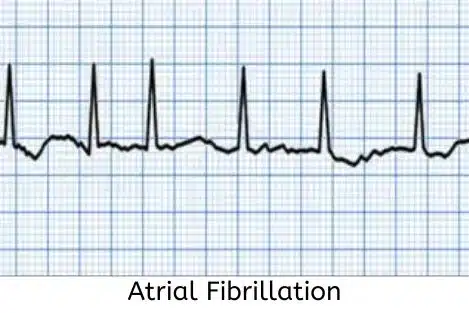
Symptoms of AF include palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Treatment options for AF include medications to control heart rate and rhythm, blood thinners to prevent blood clots, and procedures such as cardioversion or catheter ablation.
Ventricular tachycardia (VT)
VT is a potentially life-threatening arrhythmia that originates in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles).
VT is characterized by a rapid heart rate that can cause dizziness, fainting, or cardiac arrest. It can occur in individuals with structural heart disease or a history of heart attacks.
Immediate medical attention is required for VT, and treatment options include medications, implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), or catheter ablation.
Sinus bradycardia
Sinus bradycardia is a type of arrhythmia where the heart rate is slower than the normal range. It can be caused by certain medications, hypothyroidism, or underlying heart conditions.
Sinus bradycardia may not cause any symptoms in some individuals but can lead to dizziness, fatigue, or fainting in others.
Treatment options for sinus bradycardia depend on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. In some cases, a pacemaker may be implanted to regulate the heart rate.
Bundle branch blocks
These are a specific type of conduction abnormality in the heart’s electrical system.
The heart’s electrical signals are normally transmitted through specialized pathways called bundle branches, which allow coordinated contraction of the ventricles.
In bundle branch blocks, there is a delay or blockage in one of these pathways, leading to an abnormal ECG pattern.
Bundle branch blocks can be classified as right bundle branch block (RBBB) or left bundle branch block (LBBB) or complete heart block.
RBBB
This occurs when there is a delay or blockage in the electrical signals traveling through the right bundle branch.
This results in a characteristic pattern on the ECG where the QRS complex is wider than usual.
RBBB is often benign and does not require treatment unless it is associated with other underlying heart conditions.
LBBB
This occurs when there is a delay or blockage in the electrical signals traveling through the left bundle branch. This also leads to a widened QRS complex on the ECG.
LBBB can be associated with various cardiac conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, or cardiomyopathy.
Treatment for LBBB focuses on managing any underlying conditions and may involve medications or procedures like cardiac resynchronization therapy.
Useful reference:
Mayo Clinic on Heart Arrhythmia
Conclusion
In conclusion, heart arrhythmias can present in various forms and have different implications for the functioning of the heart.
The identification and management of these arrhythmias are crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health.
ECGs play a vital role in diagnosing these conditions, allowing healthcare professionals to determine the appropriate treatment options for each individual case.
Additionally, bundle branch blocks are specific conduction abnormalities that can be identified through ECGs and may require further evaluation and management depending on associated symptoms and underlying conditions.

