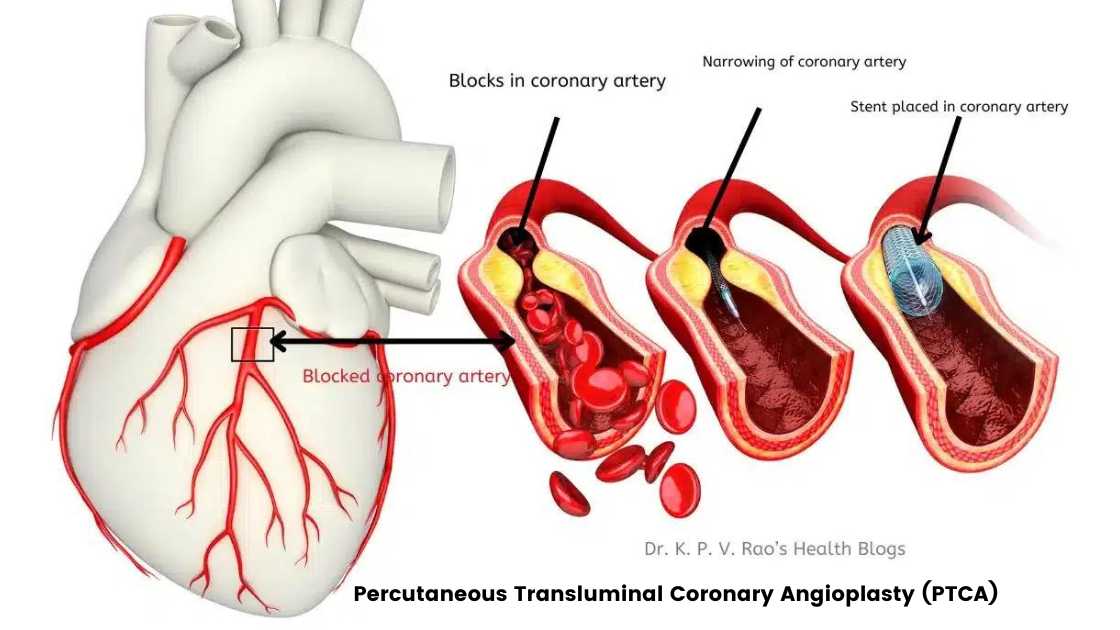
Introduction
In my last article, I described in detail what is Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty or PTCA. In this article we will learn a little bit more about it.
Benefits of PTCA
Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty or PTCA offers several significant benefits for patients with coronary artery disease.
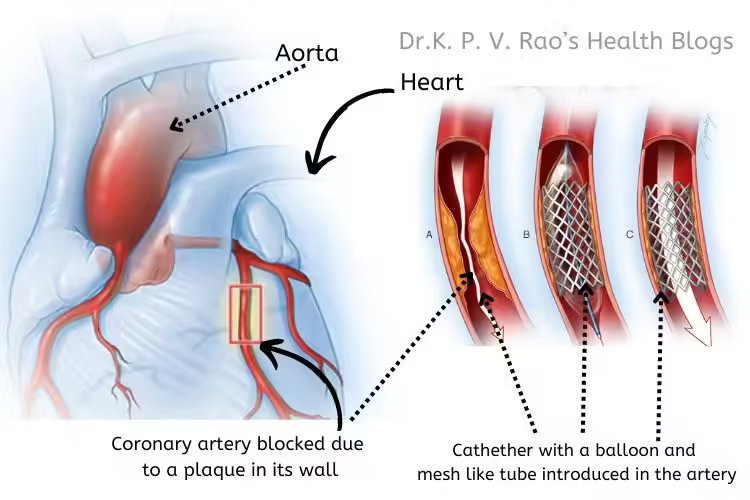
One of the foremost advantages is the improvement in blood flow to the heart muscle, which can alleviate symptoms such as chest pain (angina) and shortness of breath.
By restoring adequate blood supply, PTCA can also enhance overall heart function and quality of life. Furthermore, PTCA has the potential to reduce the risk of heart attacks, particularly in patients with severe blockages in their coronary arteries.
When compared to other treatment options like coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG), PTCA is less invasive, involving only a small incision to access the coronary arteries. This minimally invasive nature generally results in shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery times, and lower overall healthcare costs.
Additionally, PTCA can be a preferable option for patients who are not suitable candidates for open-heart surgery due to other medical conditions.
Risks of Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty
However, PTCA is not without its risks and complications. One of the primary concerns is restenosis, which is the re-narrowing of the treated artery. This can occur within months of the procedure and may necessitate additional interventions such as re-stenting or CABG.
Another risk is bleeding, particularly at the catheter insertion site, which can sometimes require medical attention.
Adverse reactions to the contrast dye used during the procedure (angiography) are also possible, especially in patients with pre-existing kidney problems or allergies.
Precautions and preventions
It is crucial to emphasize the importance of patient selection and thorough risk assessment in minimizing complications associated with PTCA. Healthcare providers must evaluate each patient’s individual risk factors and overall health status to determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
By carefully selecting candidates for PTCA and employing advanced techniques and technologies, the potential benefits of this procedure can be maximized while reducing the likelihood of adverse outcomes.
Post-Procedure Care and Long-Term Outcomes
Following a percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA), immediate post-procedure care is crucial to ensure optimal recovery and prevent complications.
Once done, patients are typically monitored in a recovery room of the hospital, where healthcare professionals closely observe vital signs and the puncture site for any signs of bleeding or other complications. It is common for patients to remain lying flat for several hours to minimize the risk of bleeding from the catheter insertion site.
Taking medications on time is a critical aspect of post-PTCA care. Patients are often prescribed antiplatelet medications, such as aspirin or clopidogrel, to prevent blood clots. These medicines play a pivotal role in maintaining the patency of the treated artery.
Additionally, lifestyle changes, including a heart-healthy diet, regular physical activity, smoking cessation, and weight management, are essential to enhance the long-term success of the procedure.
Post PTCA rehab
Cardiac rehabilitation programs, a program designed to bring back the patient to his/her normal activities, offer a structured approach to recovery, combining supervised exercise, education on heart-healthy living, and counseling to reduce stress.
These programs have been shown to improve cardiovascular fitness, reduce symptoms of heart disease, and enhance overall quality of life.
Regular follow-up appointments with a cardiologist are also imperative to monitor the patient’s progress, adjust medications as needed, and detect any signs of restenosis or other complications early.
Long-term outcomes of PTCA are generally positive, with many patients experiencing significant relief from symptoms such as chest pain and an improved quality of life. Studies indicate that the success rate of PTCA is high, with more than 90% of procedures successfully opening blocked arteries.
However, there is a risk of restenosis, where the treated artery narrows again over time. This occurs in about 20-30% of patients but can be managed with repeat procedures or additional interventions.
To maintain heart health and prevent future coronary artery disease, patients are advised to adopt and maintain healthy lifestyle practices.
This includes eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress effectively, and adhering to prescribed medications and follow-up care. By doing so, patients can significantly reduce their risk of recurrent heart issues and enjoy a better quality of life post-PTCA.
Conclusion
The importance of PTCA in modern cardiology cannot be overstated. It offers a less invasive alternative to open-heart surgery, with shorter recovery times and fewer complications.
As the prevalence of coronary artery disease continues to rise, the role of PTCA in managing this condition becomes increasingly vital.
Through ongoing research and technological advancements, PTCA continues to evolve, offering new hope and improved outcomes for patients with coronary artery disease.
Final Words
We are now coming to the end of treatment for blocked heart arteries. I hope you have gained a good amount of information regarding heart angiography as well as heart angioplasty.
My next article will be on a dietary product that is known to prevent heart disease- Olive Oil.
Adios.