Know your diabetes and live a happy, trouble-free life
Today, as I am writing this article, all over the world Diabetes Mellitus is spreading like wildfire with barely any solution to end it. What we as human beings, have achieved is control over the signs, symptoms, and complications of the disease.
Is there any way to eliminate DM? Well, as far as I have known, in all my 35 years of medical practice, you cannot do away with it totally.
But, in the early stages, also known as Impaired Glucose Tolerance or Pre-diabetes, you can prevent it from advancing to its full-fledged form. This can save one from the suffering and the cost of treatment, not to mention man-hours lost due to co-morbidities like heart failure, kidney failure, stroke, urinary tract infection, obesity, etc.
As mentioned in my last post, there are 4 types of diabetes.
In this article, I will be highlighting the signs and symptoms of DM.
The Signs and Symptoms of Diabetes-the 3 Ps
The signs and symptoms [S/S] common to all the types of diabetes are in the form of this 3 Ps: –
1] Polyuria–
This means frequent urination. A person feels like passing urine, more so at night. This disturbs the sleep of the person with diabetes.
2]Polydipsia–
This means excessive intake of water. Due to excessive urination, the diabetic patient develops mild dehydration which causes excessive thirst and drinking more and more water.
3]Polyphagia–
This means excessive hunger. Even though there is enough sugar in the blood, it is not available for uptake by tissues. This is especially so in obese patients and is called insulin resistance. The satiety center in the brain sends a signal to the digestive system to absorb more glucose and that is why one feels hungry.
The picture shown below illustrates the signs and symptoms of both Type1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-

Other common signs and symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus
Apart from these 3 major signs and symptoms [S/S] discussed above, there are many more S/S due to the co-morbidities of DM. This I will cover as we move forward.
Diabetes-Signs and symptoms-
If you look at the illustration shown above, apart from the s/s mentioned earlier[3Ps], those words shown in black are common for both types of DM. The words shown in blue will give you an idea of the other signs and symptoms of Type1 DM. Clicking on the blue words will give you the detailed information.
The Co-Morbid conditions-
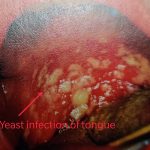
1] Yeast [candida] infections of–
a] Genitals-⇓
b] Mouth-⇓
2] Delayed healing of Wounds.
There is slow healing of wounds as there is an excess of sugar in the blood. This excess sugar is a good medium for the growth of infection-causing bacteria.
3] Nerve Problems-Neuropathy–
Due to excess sugar in the blood plasma, the myelin sheath surrounding the nerves coming out from the spinal cord undergoes degeneration. This causes tingling/pinprick sensation and numbness in the area supplied by these nerves. This occurs mostly in the limbs, more so in the legs.
4] Obesity/overweight.
The excess sugar in the blood, which is not utilized by tissues due to insulin resistance in Type2 diabetes get converted into fats. It is stored in fatty tissues in the abdomen causing a rise in the girth of the abdomen gradually. This is called Central Obesity. This leads to a substantial increase in weight causing other problems like breathlessness, an increase in BP, arthritis, etc.
5] Blurring of vision
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to blurring of vision due to changes like opacity in the lens of the eye leading to early cataract. The nerve supply of the eyes can also get affected causing blindness- a condition called retinopathy.
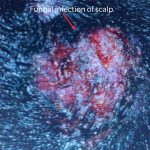
6]Fungal infection
Fungal infection of nails[onychomycosis] and scalp[tinea capitis], as shown below are very common in both types of diabetes. They are stubborn infections and take a lot of time to heal.
7] Microalbuminuria–
This is passing of proteins in the urine. Diabetes mellitus in the long run affect the kidney also. They manifest as a decrease in the filtration rate, known as GFR. This ultimately causes a condition called nephropathy which leads to Chronic Kidney disease or Kidney failure.
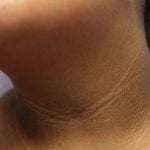
8] Acanthosis nigricans–
There is a darkening or velvety appearance of the skin in areas like axilla, nape of the neck known as Acanthosis Nigricans.
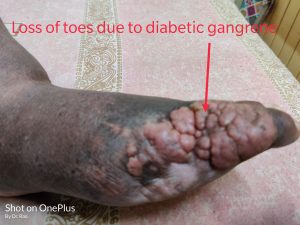
9] Gangrene of feet-
Diabetes causes a condition called diabetic microangiopathy which leads to loss of blood supply to fingers and toes. This causes swelling and infection of the feet.
Sometimes you need amputation of the gangrenous part like the picture shown here⇒
The picture shown here is of one of my patients who had to undergo amputation of the toes due to severe infection leading to gangrene. Had it not been amputated, the patient would have lost his foot and probably his whole leg.
Conclusion-
Some of the S/S is a part of complications of Diabetes, which I will discuss in detail when I come to the complications part of the series.
Depending upon the signs and symptoms of diabetes your doctor will initiate the appropriate treatment. Patients should comply fully and follow the instructions of his/her family physician. This will get the best results and prevent complications of diabetes.
Next in line–
Having said this, we will now proceed to find out what are the lab tests we have to carry out to confirm if one is a diabetic:-
1] Blood sugar fasting and post-lunch;
2] Hba1c [glycoslated haemoglobin];
3] C-peptide test to know the level of insulin in the blood and the health of the pancreas.
4] Serum insulin level to know whether it is Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes in adults.
We will study the interpretation and implications of these tests in Part 4 of this series.
Some more knowledge on Diabetes-
- Type 1 Diabetes- Click here to read-https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/type-1-diabetes
- Signs and symptoms of Diabetes-Click here to read-https://www.medicinenet.com/diabetes_mellitus/article.htm
Before we go to the next article, listen to this interesting podcast on Type 2 diabetes-


![Diabetes Mellitus-Know the signs and symptoms 3 Fungal[yeast] infection of genitals in diabetes mellitus](https://raodoctor.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/Genital-yeast-infection-e1560047314961-150x150.jpg)