What is electroencephalogram?
An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the brain using electrodes placed on the scalp.
What is an electroencephalogram used for?
The test detects abnormalities in brain waves or the electrical activity of the brain, which can help diagnose several types of brain disorders, especially someone has epilepsy.
How do you get an electroencephalogram?
The electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying brain tissue, and the recordings made by the electrodes on the surface of the scalp vary in accordance with their orientation and distance to the source of the activity.
The value recorded is distorted by intermediary tissues and bones, which act in a manner akin to resistors and capacitors in an electrical circuit. This means not all neurons will contribute equally to an EEG signal, with an EEG predominately reflecting the activity of cortical neurons near the electrodes on the scalp ³.
What are the patterns of waves seen in a healthy individual?
A healthy human EEG will show certain patterns of activity that correlate with how awake a person is.
The range of frequencies one observes are between 1 and 30 Hz, and amplitudes will vary between 20 and 100 μV.
The observed frequencies are subdivided into various groups:
- alpha (8–13 Hz),
- beta (13–30 Hz),
- delta (0.5–4 Hz), and
- theta (4–7 Hz)
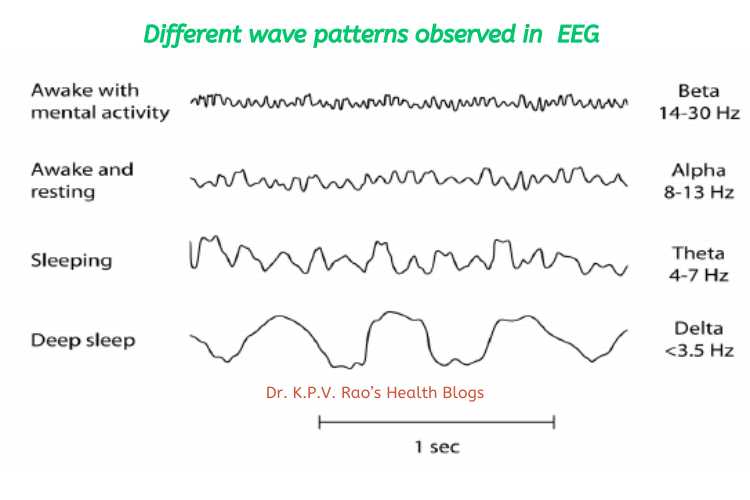
What do these wave patterns indicate?
Alpha waves are observed when a person is in a state of relaxed wakefulness and are mostly prominent over the parietal and occipital sites.
During intense mental activity, beta waves are more prominent in frontal areas as well as other regions.
Theta and delta waves are not seen in wakefulness, and if they are, it is a sign of brain dysfunction ³⁵.
How does your doctor interpret these results?
During an EEG, your healthcare provider typically evaluates about 100 pages or computer screens of activity.
He or she pays special attention to the basic waveform but also examines brief bursts of energy and responses to stimuli, such as flashing lights.
Evoked potential studies are related procedures that also may be done. These studies measure electrical activity in your brain in response to stimulation of sight, sound, or touch.
Useful resource:
(1)John Hopkins Medicine: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/electroencephalogram-eeg
(2) EEG Test (Electroencephalogram): Purpose, Procedure, & Results – WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/epilepsy/electroencep
(3) Electroencephalography | Definition, Procedure, & Uses | Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/electroencephalography.
