Part 2- Diagnosis, treatment, complications and prevention of retinal detachment
In my previous article in Part 1 of this series, I have discussed anatomy, the causes and signs and symptoms of retinal detachment. If you not read it yet, here is the link to that article-
In Part 2 of this series, we will discuss the methods to diagnose, treatment options, complications and ways to prevent this condition.

We will also discuss two patients with retinal detachment who visited me recently, and how they got themselves treated.
Case Study 1.
This 70-year-old patient who had been under treatment for hypertension for past 10 years, had retinal detachment that was diagnosed in July 2023 has undergone successful Pnuematic Retinopexy [described below]. His eyesight has improved, and he is recovering very well.
Case Study 2.
This is another 70-year-old case, Mr. JRM, who was diagnosed with severe retinal detachment, one and half years ago post-cataract surgery, was treated with laser therapy [described below]. His vision has recovered partially to an extent that he can do his daily routine easily.
Diagnosing Retinal Detachment
If you experience any symptoms suggestive of retinal detachment, it is important to consult an eye care professional promptly. They will conduct a comprehensive eye examination to assess the health of your retina and confirm the diagnosis. The examination may include the following procedures:
- Visual Acuity Test:
- This test measures how well you can see at various distances and helps determine if any visual impairment is present.
Dilated Eye Examination:
During this examination, eye drops are used to dilate your pupils, allowing the eye care professional to examine the inside of your eye, including the retina.
They will use specialized instruments and a bright light to carefully examine the retina for any signs of detachment, tears, or holes.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT)This is a noninvasive imaging method that uses reflected light to create pictures of the back of your eye. It can be used to diagnose and manage diseases like diabetes-related retinopathy and glaucoma.
OCT is an imaging method used to generate a picture of the back of your eye, called your retina. The noninvasive method produces an image by measuring the amount of a dim red light that reflects off of your retina and optic nerve.
With OCT, your ophthalmologist can see each of the retina’s distinctive layers. This allows your ophthalmologist to map and measure their thickness.
- Ultrasound Imaging: In some cases, ultrasound imaging may be used to visualize the retina if the view is obstructed due to bleeding or clouding of the eye’s media, such as in cases of severe trauma.
Based on the findings from these examinations, the eye care professional can confirm the diagnosis of retinal detachment and determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment of Retinal Detachment
A detailed description of various treatments for retinal detachment is out of scope of this article. However, I will mention in brief what to expect from your eye surgeon if he has detected retinal detachment in your eyes-
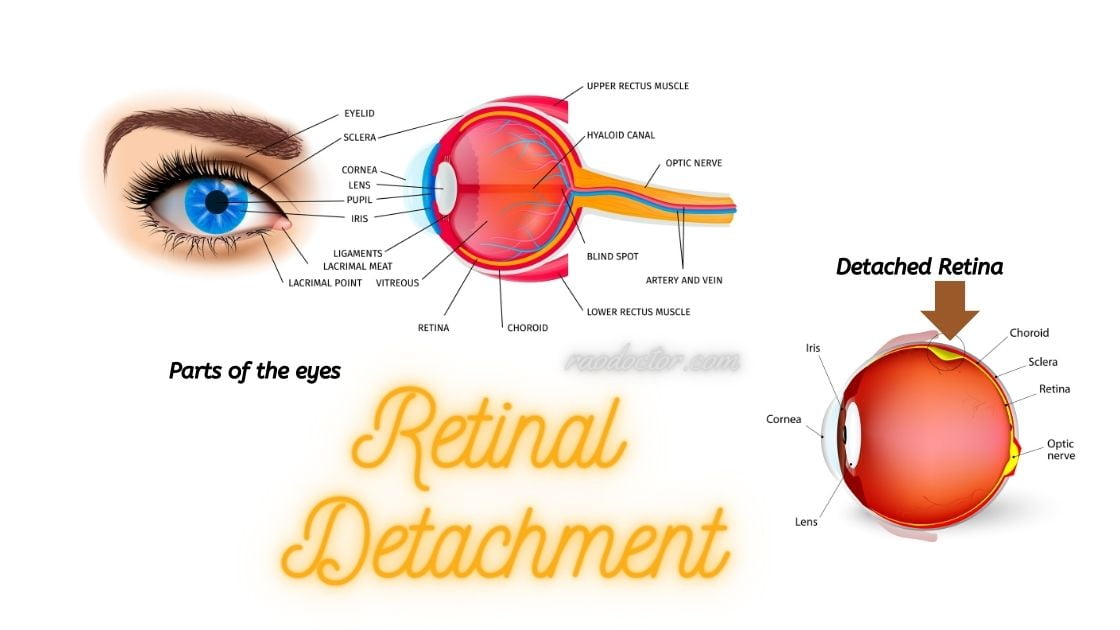
As you have already learned, retinal detachment is a condition in which the retina gets pulled away from its normal position.
It requires immediate medical attention as late treatment may lead to serious damage. There are different methods of treatment for retinal detachment, which include:
- Laser surgery: A laser beam is used to burn the retinal tear that further welds into underlying tissue.
- Freezing (Cryopexy): A freezing probe is directly applied over the tear causing a scar that helps retina secure to the eye wall.
- Pneumatic retinopexy: In the case of a small tear, a tiny gas bubble is inserted into the vitreous that will seal the tear.
- Scleral buckle: A silicon band is sewed around the white of the eye. This pushes it towards the tear until it heals.
- Vitrectomy: It is required in case of large tears where vitreous is removed and replaced with saline solution.
As detailed study of all these methods are quite exhaustive, I will leave a link to these treatments for you to explore and understand.
Treatment Options for Retinal Detachment
Prompt treatment is crucial in cases of retinal detachment to prevent further vision loss and preserve the health of the retina.
The treatment options for retinal detachment may vary depending on the severity and extent of the detachment.
In general, the aim of treatment is to reattach the retina and restore its proper function. Let’s explore some of the available treatment options:
Surgical Intervention for retinal detachment
Surgical intervention is often necessary to repair retinal detachment. There are several surgical techniques used to reattach the retina, including:
Scleral Buckling:
This procedure involves placing a silicone band around the eyeball, which pushes the wall of the eye inward, closer to the detached retina. The band helps relieve tension on the retina and allows it to reattach.
Vitrectomy:
In a vitrectomy, the vitreous gel inside the eye is partially or completely removed. This allows the surgeon to access the retina and repair any tears or holes. The vitreous is then replaced with a gas bubble or silicone oil to keep the retina in place while it heals.
Pneumatic Retinopexy:
This procedure involves injecting a gas bubble into the eye, which helps push the detached retina back into place.
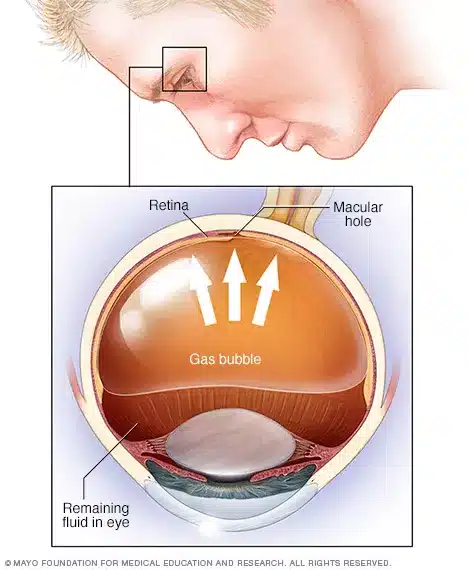
Laser or cryotherapy is then used to seal any tears or holes in the retina. The gas bubble gradually dissipates over time.
Laser Therapy for retinal detachment
Laser therapy, also known as photocoagulation, is a non-surgical treatment option for certain types of retinal detachment. This procedure uses a laser to create small burns around the retinal tears or holes. The burns create scar tissue, which helps seal the retina to the underlying layers, preventing further detachment.
Laser therapy is often used in combination with other surgical techniques to achieve optimal results.
Cryotherapy for retinal detachment
Cryotherapy is another non-surgical treatment option for retinal detachment. This procedure involves freezing the area around the retinal tears or holes using a specialized probe.
The freezing temperatures create scar tissue, which seals the retina to the underlying layers, promoting reattachment.
Cryotherapy may be used as a standalone treatment or in combination with other surgical techniques.
The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the location and extent of the detachment, the presence of associated complications, and the individual’s overall eye health. Your eye care professional will recommend the most suitable treatment option for your specific case.
Useful links:
- Patient Info
- National Eye Institute
- Mayo Clinic
Recovery and Rehabilitation after Retinal Detachment Treatment
After undergoing treatment for retinal detachment, proper recovery and rehabilitation are essential to optimize visual outcomes.
Following any surgical procedure, your eye care professional will provide specific post-operative instructions, which may include:
- Using prescribed eye drops to prevent infection and aid healing
- Avoiding activities that can increase eye pressure, such as heavy lifting or straining
- Wearing an eye patch or shield to protect the eye during the initial healing phase
- Attending follow-up appointments to monitor progress and ensure proper healing
It’s important to adhere to these instructions and communicate any concerns or changes in your vision to your eye care professional.
The recovery period can vary depending on the severity of the detachment and the treatment received. It may take several weeks to months for the retina to fully heal, and vision improvements may continue over time.
During the recovery phase, it’s crucial to take care of your overall eye health. This includes practicing good hygiene, avoiding rubbing or touching your eyes excessively, and following a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet and regular exercise.
By adopting these habits, you can support the healing process and reduce the risk of complications or future detachments.
You can learn more about these various treatments in detail here-
Procedures to Treat Retinal Tears & Retinal Detachments
Complications and Long-Term Effects of Retinal Detachment
Although prompt treatment increases the chances of successful reattachment, there can be complications and long-term effects associated with retinal detachment. Some potential complications include:
Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy (PVR):
PVR is the abnormal growth of scar tissue on the surface of the retina. This scar tissue can pull on the retina, leading to re-detachment or other vision problems.
Macular Pucker:
Macular pucker occurs when scar tissue forms on the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision. This can result in distorted or blurred vision.
Macular Hole:
In some cases, the macula can develop a hole due to detachment. This can cause a significant loss of central vision.
While these complications can occur, it’s important to remember that early detection and prompt treatment can significantly reduce the risk. Adhering to the recommended follow-up appointments and maintaining good long-term eye care can help minimize the chances of complications and optimize visual outcomes.
Preventing Retinal Detachment
While some risk factors for retinal detachment, such as age or genetic predisposition, cannot be controlled, there are steps you can take to minimize the risk. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
Regular Eye Examinations:
Routine eye examinations are essential for detecting any early signs of retinal detachment or other eye conditions. Regular check-ups allow your eye care professional to monitor your eye health and address any concerns promptly.
Protecting Your Eyes:
Taking precautions to protect your eyes from trauma is crucial. When engaging in activities that pose a risk of eye injury, such as sports or construction work, wear appropriate eye protection, such as safety goggles or a face shield.
Managing Underlying Health Conditions:
If you have underlying health conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure, it is important to manage them effectively. Keeping these conditions under control reduces the risk of complications that can contribute to retinal detachment.
Seeking Prompt Medical Attention:
If you experience any sudden changes in your vision, such as flashes of light or a sudden increase in floaters, seek immediate medical attention. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve the chances of preserving your vision. By being proactive in your eye health, you can reduce the risk of retinal detachment and maintain the best possible vision for years to come.
Conclusion
Retinal detachment is a serious eye condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing the available treatment options, you can take an active role in preserving your precious sight.
Regular eye examinations, especially if you have any risk factors, are crucial for early detection and intervention.
If you experience any sudden changes in your vision, do not hesitate to seek immediate medical attention.
Final Words
Remember, your eyes are irreplaceable, and taking proactive steps towards eye health is a key investment in your overall well-being.
If you have found this article useful, do consider sharing it with people you know using the social media icons at the base of this article. If you have a Twitter [ now X] account, you can Click to Tweet below:
Retinal Detachment-Diagnosis and Management Share on XMy next article will be on an important heart investigation- Echocardiography.