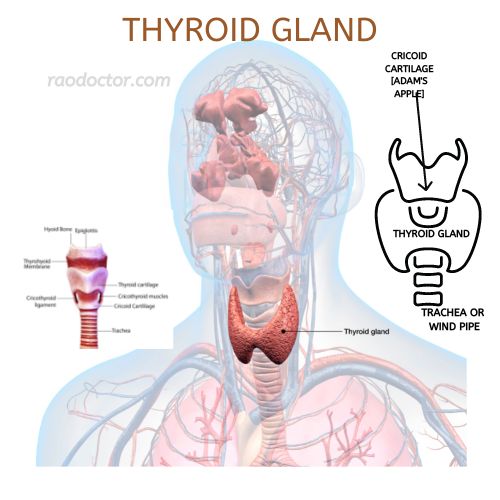

The thyroid gland is another very important gland in our body after the pancreas. It is also known as the powerhouse that drives our daily bodily function by providing or fueling energy to our tissues and organs.
Of late a lot of people are visiting my clinic with signs and symptoms of dysfunction of the thyroid gland. Thyroid disease is the second most common hormonal disease after Diabetes.
According to the British Medical Magazine, the Lancet, there are about 200 million people suffering from this disease globally.
Hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and an assortment of less common thyroid conditions can all have a significant impact on your quality of life.
What is Thyroid Gland?
What is the thyroid gland? It’s a small but mighty organ that sits in the front middle of your neck on either side of your larynx (aka voice box). In fact, it’s so small you probably didn’t even realize there was another organ in that area until you started Googling “that weird thing in the front of my neck.”
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland [have a look at the picture at the top] that produces important hormones called T3 and T4 [Short for Triiodothyronine and Tetraiodothyronine], collectively called as Thyroxine.
Thyroid Gland – What is it and why is it important? Share on XThese hormones are essential for energy production by fueling our red blood cells, activating carbohydrates for energy, regulating protein use for growth and maintenance of good bone density.
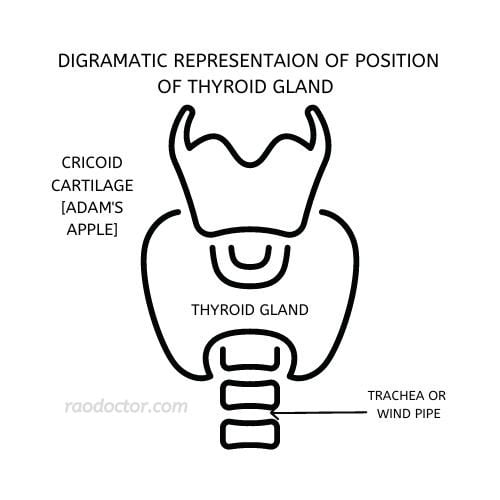
It also has a significant effect on metabolism by regulating the rate at which we burn calories. The thyroid gland is controlled by the hypothalamus in the brain and the pituitary gland at the base of the brain, the hypothalamus- pituitary axis which releases thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH).
The TSH travels to the thyroid gland and triggers the production of thyroid hormones. Slightly more than half of your body’s supply of thyroid hormone is produced by your thyroid gland, while the rest is produced by your body’s liver by activating the inactive T4 to T3.
What are the hormones produced by thyroid gland?
The thyroid gland produces two types of hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Both of these hormones are necessary for the body to function properly.
T3 and T4 are responsible for regulating metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature, as well as controlling how quickly the body burns calories.
However, T3 is more biologically active than T4. This means that T4 is the precursor to T3, meaning that it must be transformed into T3 before it can have any biological effect.
This transformation occurs within the tissues that are affected by T3. It is important to note that T4 is the main form of thyroid hormone found within the blood.
This makes it the most commonly tested hormone when assessing thyroid function. On the other hand, T3 is the most biologically active form of thyroid hormone, as well as the form that is measured when testing for Reverse T3 (RT3).
What is the Role of Thyroid Hormones in our body?
The thyroid gland is responsible for the production of hormones that regulate metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature. Metabolism is the process by which cells break down food and substances like alcohol into glucose, which is used as energy by the cells.
The thyroid gland produces two types of hormones. These hormones are necessary for the body to function properly: Triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4).
What is the effect of T3 and T4 hormones on different parts of our body?
- These hormones control metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature, as well as the rate at which the body burns calories. –
- Thyroid hormones help the body use energy from carbohydrates and fats by regulating metabolism.
- They also promote normal development during infancy and childhood.
- Normal thyroid function is important for the development of brain and nerve cells. During infancy and childhood, normal thyroid function is important for normal growth and development of the skeleton.
- Thyroid hormones also have an effect on protein metabolism. They are important for maintaining healthy bones and muscles. –
- Thyroid hormones are important for the regulation of heart rate.
- Normal thyroid function is important for regulating body temperature.
- Thyroid hormones also have an effect on energy production in the cells.
- Normal thyroid function is important for appetite, weight, and general well-being.
What happens if the Thyroid Hormones are produced in excess or if they are deficient?
Diseases of the thyroid are caused by either excessive or less production of thyroid hormones. As mentioned above, there are important hormones- T3 and T4. And the hormone that controls the production of these hormones-TSH.
Signs and symptoms of thyroid disease can be summarized as shown below-

Excess Production of Thyroid Hormones:
People who produce excessive amounts of thyroid hormones have an overactive thyroid gland. The medical term for this condition is hyperthyroidism.
Thyroid storm
Sometimes the thyroid hormones are so much in excess that they cause what is known as the thyroid storm.
Hyperthyroidism can cause symptoms such as-
- rapid heartbeat,
- sweating,
- muscle weakness,
- tremors of hands and tongue
- and trouble sleeping.
Deficient Production of Thyroid Hormones:
People who produce insufficient levels of thyroid hormones have an underactive thyroid gland. The medical term for this condition is hypothyroidism.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism include-
- weight gain,
- trouble sleeping,
- muscle weakness,
- and feeling tired.
Enlarged thyroid- the Goiter
If your thyroid gland produces too few thyroid hormones, you may develop goiter, which is a swelling in your neck caused by an enlarged thyroid gland. This is called a goiter. The enlargement is caused by an increased need for thyroid hormone compared to the amount of hormone being produced. Iodine deficiency can cause goiter.
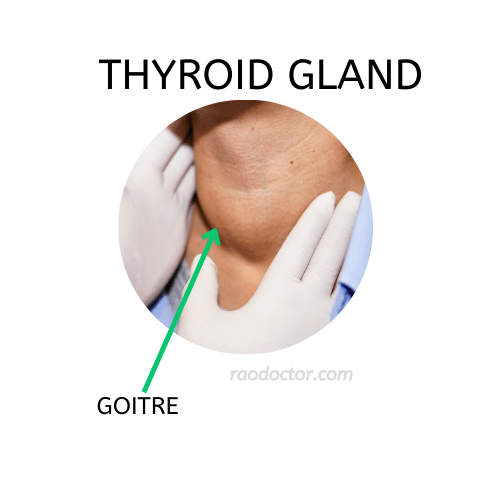
Most people with a goiter will have an enlarged thyroid gland. Although the goiter is usually painless, it can cause significant problems in rare cases.
If a goiter is large enough, it can push your voice box forwards, causing shortness of breath and a cough if you have frequent mucus in your throat. A goiter can also cause pressure on your food pipe [esophagus] and make it difficult to swallow.
What is a thyroid nodule?
Sometimes you can see some node like swelling in thyroid of some people. This is called thyroid nodule formation. It’s not cancer, but it is a marker of low thyroid function. If nodules are large enough, you may feel a lump in your neck.
Diseases Of Thyroid Gland
There are 2 main diseases of the thyroid gland. They are-
Hypothyroidism: An underactive thyroid gland
An underactive thyroid gland (called hypothyroidism) is the most common thyroid condition and occurs when the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough hormones.
This can happen for one of two reasons: the thyroid gland is not making enough thyroid hormone or the tissues in the body are not able to use the thyroid hormone as effectively as they normally would.
Learn more about hypothyroidism here-
Hyperthyroidism: An overactive thyroid gland
An overactive thyroid gland (called hyperthyroidism) is a condition in which the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. The most common cause is an autoimmune disorder called Graves’ disease.
Learn more about hyperthyroidism here-
Hashimoto’s Thyroid disease
This is an autoimmune disease that causes hypothyroidism. To learn more about Hashimoto’s disease, click here- Hashimoto’s Disease
How would you know if you have either of these thyroid diseases?
The diagnosis of hypothyroidism is based on the results from the clinical examination, blood tests, and thyroid function tests.
Thyroid function tests measure levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) in the body and TSH [thyroid stimulating hormone] by getting a blood test.
The normal values are as follows-
The normal level for both is-
- T3-1 to 5 mU/L
- T4-15 to 50 U/L .
- Free T3– 0.9 to 3 mU/L
- Free T4-0 to 8 U/L.
- TSH-0.5 t0 5.5ng/ml
Learn more about these investigations and their interpretations Click here.
Thyroid Nodules-
These nodules are small growths in the thyroid gland. To diagnose these, we have thyroid scans or ultrasonography as shown below-
A low level of one or both of these hormones indicates hypothyroidism. A diagnosis of hypothyroidism is confirmed by a doctor who can see that symptoms are relieved with treatment. There are several types of thyroid tests available: Free T4 = Thyroxine bound to carrier proteins.
It is not measured in most labs, but this should be done if a patient has been on medication for a long time and their free T4 levels are decreasing despite treatment; alternatively, it can be used to look at the effects of the medication itself on the body.
Cancer of the thyroid
This is an excessive growth of thyroid that can spread to other parts of our body and cause total disruption of our bodily functions.
Useful Resources-
Summary
People who produce excessive amounts of thyroid hormones have an overactive thyroid gland. An overactive thyroid gland is called hyperthyroidism.
An underactive thyroid gland is called hypothyroidism. Hyperthyroidism can cause symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, sweating, muscle weakness, and trouble sleeping.
Hypothyroidism can cause symptoms such as weight gain, trouble sleeping, muscle weakness, and feeling tired.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should see your doctor to see if you have a thyroid condition. Your doctor will do a physical exam and may order lab tests to help diagnose the condition. Your doctor may also recommend that you get a thyroid scan.
If you have liked this Article-
Please share it on Twitter-
Thyroid Gland-What is it and Why is it Important? Share on X