A Guide to Intermittent Lumbar Traction, IFT, and SWD
If you prefer listening to this article, you can do so here-
Physiotherapy of Backache-an overview
Severe backache is a common ailment that affects individuals across various age groups and lifestyles. One of the treatments suggested by an orthopedic surgeon is physiotherapy for backache.
It can arise from several causes, including but not limited to muscular strain, herniated discs, arthritis, and poor posture. These underlying factors contribute to significant discomfort, limiting mobility and affecting daily activities.
My story
In August 2024, I had a severe backache that would not respond to medications alone. So I consulted a orthopedic surgeon friend of mine, who after going through my x-ray reports suggested 3 types of physiotherapies as described below.
In my opinion, if one does not get relief from backache by medicines alone, they should consult their family physician for proper advice.
Muscle spasms and inflammation often accompany back pain, which can further exacerbate symptoms and negatively impact overall quality of life.
The symptoms associated with severe backache can vary in intensity and may include pain that radiates down the legs, stiffness, and a reduced range of motion, meaning you are having difficulty in simple acts like getting up from bed or from a chair.
Individuals often report that their pain increases with certain activities, such as prolonged sitting or standing.
In some cases, back pain may be so debilitating that it interferes with work, social interactions, and personal responsibilities, leading to feelings of frustration and emotional distress. I felt the same for two weeks.
Given the complexity of back pain, it is crucial to seek medical advice for persistent or severe symptoms.
When to visit your family physician in a backache?
Your doctor can evaluate the specific nature of backache, identifying potential causes and recommending appropriate interventions. Initially, he may suggest conservative approaches that might include rest, ice, heat application, and over-the-counter pain relief.
However, in many cases of unrelieved pain, physiotherapy emerges as a vital component of treatment.
Therapeutic techniques, such as intermittent lumbar traction, interferential therapy (IFT), and shortwave diathermy (SWD), can facilitate healing, reduce pain, and restore normal function.
Furthermore, physiotherapy not only addresses immediate pain relief but also emphasizes the importance of rehabilitation.
Through customized exercise programs, patients learn strategies to strengthen the back and improve flexibility, which are essential in preventing future episodes of pain.
Ultimately, a multidisciplinary approach that includes physiotherapy may be beneficial for individuals struggling with severe backache, offering a pathway towards faster recovery and enhanced well-being.
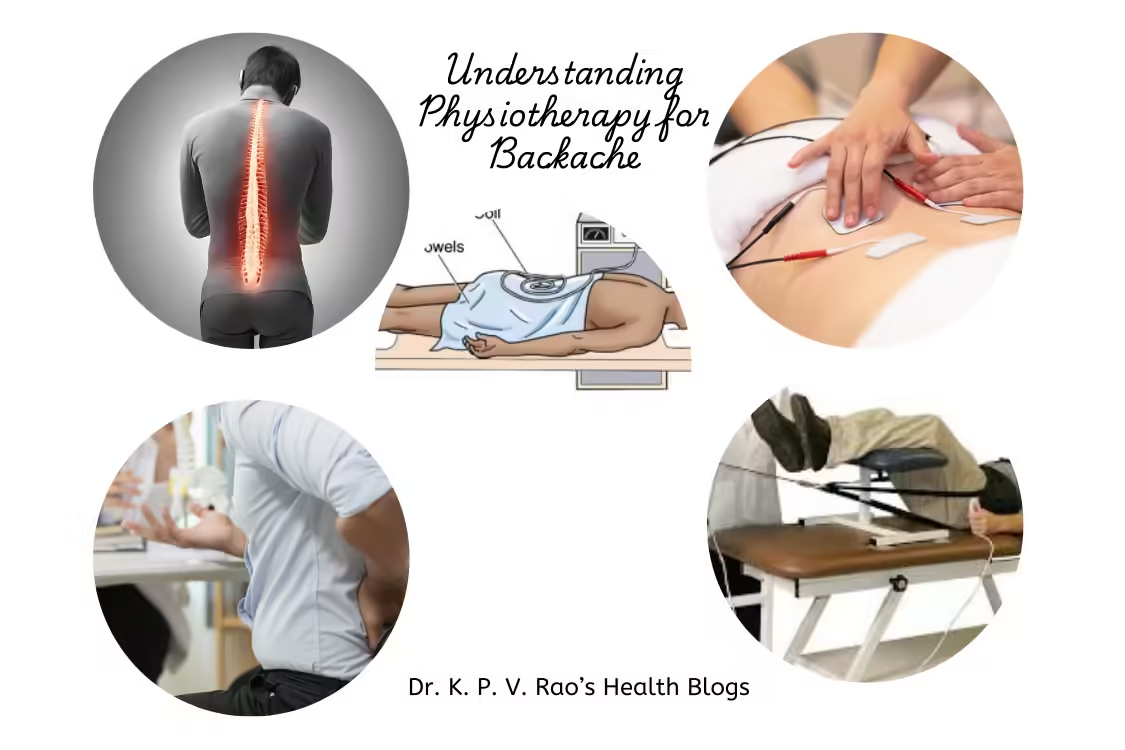
Physiotherapy for backache- Intermittent Lumbar Traction
Intermittent lumbar traction is a specialized physiotherapy technique designed to alleviate back pain by applying a pulling force to the spine.
This method utilizes mechanical devices that create a gentle and controlled decompression effect on the lumbar vertebrae.
The primary goal of this treatment is to relieve spinal pressure, which can effectively reduce pain and improve overall mobility for individuals experiencing severe backache.
The mechanics behind intermittent lumbar traction involve alternating periods of pulling and resting, which helps to create a negative pressure within the spinal discs.
This negative pressure encourages the retraction of herniated or bulging discs, facilitating the movement of nutrients and fluids into the affected area, promoting healing.
The equipment used for this therapy typically consists of a traction table, which supports the patient while delivering the necessary force to stretch the spine in a secure manner.
Physiotherapy interventions, such as intermittent lumbar traction, have been shown to provide various physiological benefits.
Patients often experience immediate relief from pain, reduction of muscle spasms, and enhanced range of motion following treatment.
By relieving pressure on spinal nerves and improving circulation in the affected region, this form of therapy also aids in reducing inflammation and promoting tissue repair.
Consequently, individuals suffering from chronic back pain may find this treatment option particularly beneficial, as it not only addresses pain relief but also contributes to long-term recovery.
Moreover, incorporating intermittent lumbar traction into a comprehensive physiotherapy regimen can empower patients to return to their daily activities more quickly and with less discomfort.
As a result, understanding and utilizing this effective therapeutic approach is essential for those dealing with debilitating back issues.
Understanding IFT and SWD Therapies
Interferential Therapy (IFT) and Short-Wave Diathermy (SWD) are two advanced physiotherapy modalities designed to enhance recovery from back pain, specifically when coupled with lumbar traction.
IFT
IFT utilizes electrical currents to stimulate tissues, promoting pain relief and facilitating healing.
This therapy effectively penetrates deep into the tissues, allowing for a targeted approach in alleviating discomfort associated with muscular and joint issues.
By creating a higher frequency interference pattern, IFT can mitigate pain while minimizing the sensation of electrical stimulation on the skin.
SWD
On the other hand, Short Wave Diathermy employs high-frequency electromagnetic waves to generate heat in the deeper layers of tissue.
This increased thermal energy promotes increased blood flow and reduces muscle spasms, thus aiding in the relaxation of tight muscles.
SWD is particularly beneficial in treating chronic conditions, where the sustained heating effect can greatly enhance mobility and accelerate recovery times. When combined with physiotherapy interventions such as intermittent lumbar traction, these therapies can significantly improve patient outcomes.
The physiological effects of both IFT and SWD include enhanced circulation, which plays a crucial role in delivering nutrients and removing waste products from the damaged tissues. Furthermore, these therapies support muscle relaxation, enabling patients to engage more effectively in their rehabilitation exercises. By integrating IFT and SWD as complementary treatments, physiotherapists can create a comprehensive therapeutic regimen that addresses various aspects of backache, ultimately contributing to improved quality of life for individuals suffering from chronic pain.
In conclusion, the combination of physiotherapy modalities, including intermittent lumbar traction alongside IFT and SWD, offers a promising approach to managing back pain more holistically and effectively.
Session Guidelines and Therapy Duration
When seeking relief from backache through physiotherapy, understanding the recommended duration and frequency of therapy sessions is crucial for optimal recovery.
The effectiveness of treatments such as intermittent lumbar traction, Interferential Therapy (IFT), and Shortwave Diathermy (SWD) can significantly depend on adhering to a structured therapy plan guided by healthcare professionals.
Sessions Duration
Typically, physiotherapy sessions for treating back pain are recommended to last anywhere from 30 to 60 minutes. This duration allows for both the execution of specific techniques, such as IFT, and the necessary follow-up exercises designed to strengthen and support the back.
For therapies like intermittent lumbar traction, the treatment duration can vary based on individual needs, but generally, sessions last around 15 to 30 minutes, depending on the intensity and goal of the therapy.
For optimal results, it is advisable to undergo physiotherapy sessions two to three times a week. This frequency helps in maintaining the momentum of recovery, enabling the body to gradually respond to the treatments.
Adequate consistency in attending these sessions is vital for addressing the underlying issues contributing to backache.
How many sessions should one have for physiotherapy of backache?
The total duration of the physiotherapy treatment can vary depending on individual circumstances, such as the severity of the condition and the body’s responsiveness. Generally, a treatment plan may span from four to eight weeks.
Regular assessments by a physiotherapist will help determine if adjustments in therapy duration or frequency are necessary to further enhance the recovery process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, following prescribed session guidelines and therapy duration for physiotherapy is essential in managing back pain effectively.
Engaging in this structured approach will maximize the benefits of treatments like intermittent lumbar traction, IFT, and SWD, ultimately leading to improved outcomes for individuals suffering from backaches.
Final words
In the end, I would like to inform you that after 10 days session of my physiotherapy, I got total relief from backache.
I suggest, for all those having a nagging backacke, to visit their family physician and take their opinion regarding the physiotherapy for backache suggested in this article.
Adios.