Introduction
In today’s fast-paced world, medical imaging has become a crucial aspect of healthcare. It allows doctors to diagnose diseases and conditions quickly and accurately, helping them to determine the best course of treatment for their patients.
From X-Rays to MRIs, there are various imaging techniques used in healthcare, each with its unique advantages and limitations. These techniques allow healthcare professionals to see inside the human body without invasive procedures, leading to earlier diagnoses and better outcomes.
In this article, we’ll explore the various imaging techniques used in healthcare, how they work, and what makes each technique unique. I have shown some of them below-

Whether you’re a healthcare professional or a curious patient, this article will give you a better understanding of the medical imaging techniques that are essential in modern healthcare.
What are the 5 imaging techniques?
The following five imaging techniques are frequently used by doctors all over the world. They are:
- X-Rays,
- CT scan,
- MRI,
- Ultrasound and
- Pet scan or Nuclear scan
So, let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of these five medical imaging techniques together!
X-ray imaging – how it works and applications
X-ray was the first imaging technique used in medical healthcare. It was discovered by the German physicist Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen on 8th of November 1895. Ever since then, x-rays have been used in diagnosing many diseases in our modern-day healthcare system.
How is X-ray done?
Live screening of a patient using an X-ray machine involves a series of steps to ensure accurate and real-time imaging. First, the patient is positioned on an examination table or stand according to the area to be screened.
Next, the X-ray machine is adjusted to the appropriate settings, such as energy level and exposure time, to capture the desired images. The X-ray technician then activates the machine, and a controlled amount of radiation is emitted towards the patient’s body.
As the X-rays pass through the patient, they are absorbed or scattered by different tissues, creating an image on a digital detector or film. This image is instantly displayed on a computer screen, allowing the technician and medical professionals to view and analyze it in real-time.
This live screening using an X-ray machine enables quick and accurate diagnosis of various medical conditions, aiding in effective treatment planning and monitoring of patients’ health.
How do X-rays help in diagnosing a disease or ailment?
X-ray imaging is one of the most commonly used imaging techniques in healthcare. It uses electromagnetic radiation to produce images of the inside of the body.
When an X-ray beam is directed at the body, some of the radiation is absorbed by the body’s tissues, while the rest passes through and is detected on the other side.
The amount of radiation absorbed by the body’s tissues depends on the density of the tissue.
Bones, for example, absorb more radiation than soft tissue, which is why they appear white on X-ray images.
X-ray imaging is used to diagnose a variety of conditions, including
- broken bones or fractures
- dental problems such as caries, malalignment of teeth, etc. Sometimes your dentist may order a special x-ray known as the OPG [Orthopantomagrams] as shown in the first picture.
- certain lung conditions.
- Urinary stones.
It is also used to screen for certain cancers, such as breast cancer, by producing mammograms.
What are the limitations of X-rays?
However, X-ray imaging has some limitations. It cannot produce detailed images of soft tissue, which can make it difficult to diagnose certain conditions.
Additionally, X-rays use ionizing radiation, which can be harmful in large doses.
Computed Tomography (CT scan) – how it works and applications
Computed tomography (CT) imaging, also known as a CT scan, is a more advanced imaging technique than X-ray.
It uses X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed images of the inside of the body.
During a CT scan, the patient lies on a table that moves through a doughnut-shaped machine that takes X-ray images from different angles. A computer then combines these images to produce a detailed 3D image of the body’s internal structures.

CT scan is used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, including cancer, heart disease, and bone fractures.
It is also used to guide procedures such as biopsies and surgeries. CT imaging produces more detailed images than X-rays and can identify smaller abnormalities in the body.
However, like X-rays, CT scan uses ionizing radiation, which can be harmful in large doses.
Additionally, CT scans are more expensive than X-rays and take longer to perform.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – how it works and applications
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive imaging technique that uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves, and a computer to produce detailed images of the body’s internal structures.
During an MRI, the patient lies on a table that moves through a cylindrical machine.
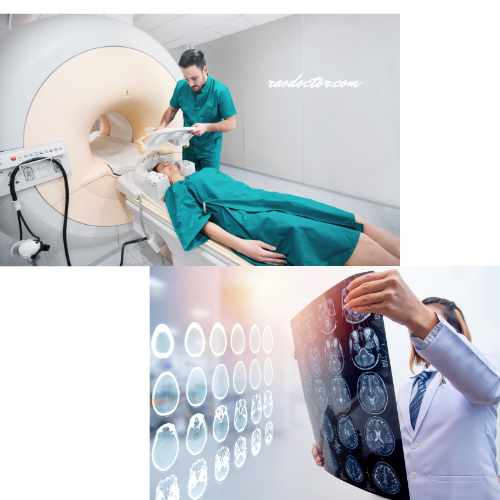
The machine produces a strong magnetic field that causes the hydrogen atoms in the body’s tissues to align in a certain way.
Radio waves are then directed at the body, causing the hydrogen atoms to emit signals that are detected by the machine and used to produce an image.
MRI imaging is used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, including
- brain and spinal cord injuries,
- joint injuries, and
- cancer.
It produces highly detailed images of the body’s internal structures and can identify abnormalities that may not be visible in other imaging techniques.
Additionally, an MRI scan does not use ionizing radiation, making it safer than X-ray and CT scan.
However, MRI scans are more expensive than X-rays and CT scans and can take longer to perform.
Interesting topic for you- Heart MRI
Ultrasound imaging – how it works and applications
Ultrasound imaging, also known as sonography, uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the inside of the body.
During an ultrasound, a handheld device called a transducer is moved over the body’s surface, emitting sound waves that bounce off the body’s tissues and are detected by the transducer.

A computer then uses these sound waves to produce an image of the body’s internal structures.
Ultrasound imaging is commonly used to
- monitor fetal development during pregnancy and
- diagnose conditions such as gallstones, kidney stones, and cysts.
- It is also used to guide procedures such as biopsies and surgeries.
- to diagnose liver disease, particularly non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, liver cancer and hepatitis.
Ultrasound imaging produces images in real-time and does not use ionizing radiation, making it safe for pregnant women and children. However, it has some limitations. It cannot produce detailed images of the body’s internal structures and may not be able to detect certain abnormalities.
Nuclear medicine imaging – how it works and applications
Nuclear medicine imaging is a specialized imaging technique that uses small amounts of radioactive material to produce images of the body’s internal structures. It is also known as PET scan [see below for description]
A PET scan, or positron emission tomography scan, is a medical imaging technique that uses a radioactive tracer to produce detailed images of the body’s organs and tissues. It is commonly used to diagnose and monitor various conditions, including cancer, heart disease, and brain disorders.
How is it done
The procedure involves injecting a small amount of a radioactive substance into the patient’s bloodstream.
During a nuclear medicine scan, the patient is given a small amount of radioactive material, which is absorbed by the body’s tissues.
This substance is then absorbed by the body’s tissues and emits positrons, which are detected by the PET scanner. The scanner then generates images that show the distribution of the tracer in the body [see the image below], providing valuable information about the functioning of organs and the presence of abnormalities.
Where and why are PET scans done
PET scans are typically performed in specialized imaging centers and are considered safe and minimally invasive. The results of a PET scan can help healthcare professionals make accurate diagnoses and develop appropriate treatment plans for their patients.
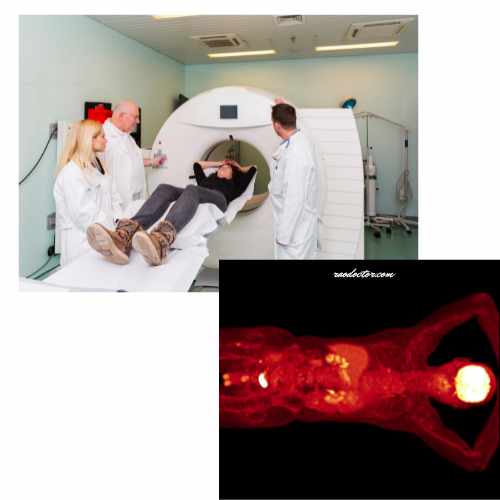
The radioactive material emits gamma rays, which are detected by a special camera and used to produce images of the body’s internal structures.
Nuclear medicine imaging is used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, including
- cancer,
- heart disease, and
- certain neurological disorders.
- It can also be used to determine the function of organs and tissues in the body.
However, nuclear medicine imaging is more invasive than other imaging techniques and involves exposure to radiation. Plus, it is very expensive.
Useful resource- Merck Manual
Advancements in medical imaging technology
Medical imaging technology is continually advancing, leading to the development of new imaging techniques and improvements in existing techniques.
For example, there are now 3D and 4D ultrasound images that provide more detailed images of the body’s internal structures. These are particularly important to diagnose any congenital defects before birth, so that the parents are aware of the condition of their child in advance. You can also use this to determine the sex of the unborn child; however, this is strictly banned in India.
Additionally, there are new MRI techniques that can produce images of the brain’s functional activity, providing valuable information for the diagnosis and treatment of neurological disorders like Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
Advances in medical imaging technology will continue to improve the accuracy and efficiency of medical diagnoses and treatments.
Benefits and Risks of medical imaging
Medical imaging has many benefits, including the ability to diagnose diseases and conditions quickly and accurately.
It also allows healthcare professionals to monitor the progress of treatments and guide procedures such as biopsies and surgeries.
However, medical imaging also carries some risks. X-ray and CT imaging use ionizing radiation, which can be harmful in large doses.
Additionally, some imaging techniques involve injection of contrast material, which can cause allergic reactions in some patients. Healthcare professionals must weigh the benefits and risks of each imaging technique before recommending its use.
Choosing the right imaging technique for your medical condition
Choosing the right imaging technique for a medical condition depends on several factors, including:
- the type of condition being diagnosed,
- the patient’s age and medical history, and
- the benefits and risks of each imaging technique.
Healthcare professionals must carefully consider these factors before recommending an imaging technique.
Patients should also be informed of the benefits and risks of each imaging technique and have the opportunity to ask questions and express any concerns they may have.
Conclusion
Medical imaging is a crucial aspect of modern healthcare. From X-Rays to MRIs, there are various imaging techniques used in healthcare, each with its unique advantages and limitations.
These imaging techniques allow healthcare professionals to diagnose diseases and conditions quickly and accurately, leading to earlier diagnoses and better outcomes for patients.
However, each imaging technique carries some risks, and healthcare professionals must carefully weigh the benefits and risks of each imaging technique before recommending its use.
Advances in medical imaging technology will continue to improve the accuracy and efficiency of medical diagnoses and treatments, leading to better outcomes for patients.
Final Words
I hope you have found this article useful. If yes, please share on the social media icons at the bottom of this article. Alternately, you can Click to Tweet here-
From X-Rays to MRIs: Exploring the Various Imaging Techniques Used in Healthcare Share on XAs with everything else in this modern world, Obesity [extremely overweight] is an ever-increasing concern that affects all aspects of health in individual lives. So, my next article will be on an interesting topic- “Can weight loss reverse the health effects of Obesity?“

