Diet In Diabetes-Part 1- Manage your blood sugar through a diet plan
Table of Contents
Introduction
Diet plays a crucial role in controlling blood sugar levels in diabetes. By making informed food choices, individuals with diabetes can manage their condition effectively.
A balanced diet consisting of adequate carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, along with portion control, can help regulate blood sugar levels.
It is important to limit the intake of sugary and processed foods, opt for whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, and include plenty of fruits and vegetables.
Management of diabetes is nothing but how you go about controlling your blood sugar levels and HbA1C levels.
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and consultation with a healthcare professional are essential for personalized dietary recommendations.
I have divided this article about diet in diabetes into two parts. In Part 1, I am going to discuss the basics of diet management and in Part 2 the type of food to eat, based on the glycemic index of the food.
In the prediabetics, the control of blood sugar and HbA1C can be done by regular exercise and a change in diet pattern.
In frank diabetes, it is
- Taking antidiabetic medicine/s on time.
- Diet, and
- Exercise
Out of these 3 things to do, I have already covered the medications part in my previous blogs-Diabetes Part 5 and Diabetes Part 6.
What Diet you should have in Diabetes-
Learning about diet in diabetes is more about what you should eat and what you should not.
As you can see above, diet plays an important role in managing all types of diabetes, be it pre-diabetes, Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes.
All diabetics need a balanced diet to maintain good health as well as control the regular surge in blood sugar.
What is a Balanced Diet?
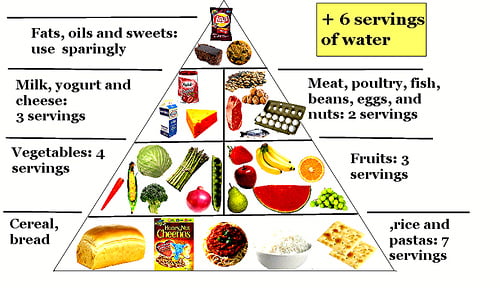
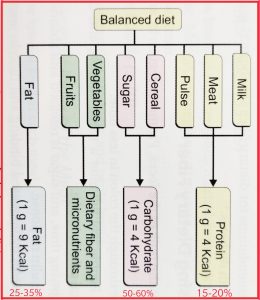
A balanced diet is the one which contains all the components of food like carbohydrates [sugar, starch, etc.], proteins, fats and fibers in a proportionate manner as shown in the diagram below: –
Factors determining Diet in Diabetes
Diet in diabetes depends on various factors, namely: –
1] Age-
Advancing age results in lesser intake of food, which is very important in elderly diabetics as they are more prone to having hypoglycemia.
Again, having a balanced diet helps in all diabetics-both the young and the elderly- by proper control of blood sugar, cholesterol, etc. and thereby maintain ideal body weight.
2] Weight-
Type 2 diabetics are mostly overweight or obese. This has led to a condition called Metabolic Syndrome or Syndrome X.
In this disease, along with diabetes, you have cardiovascular problems like hypertension, high cholesterol levels, and accumulation of fats in the trunk, popularly known as central obesity.
As mentioned above, it is beneficial to maintain the ideal body weight.
Now, what exactly is the ideal body weight?
Ideal body weight is the weight of a person which is the maximum weight of that person depending upon his/her height and build.
How do you calculate Ideal Body Weight?
Most of the research done on ideal body weight calculation emphasizes height in its calculation. You can calculate your ideal body weight by using any one of these formulae-
J. D. Robinson Formula-
a] Gents- 52 kg+1.9 kg per inch above 5 feet height
b] Ladies- 49 kg+1.7 kg per inch above 5 feet height.
D. R. Miller Formula-
a] Gents-56.2+1.41kg per inch above 5 feet
b] Ladies- 53.1kg +1.36 kg per inch above 5 feet height
You can also use this calculator for getting your stats immediately-
Calculating your ideal body weight will make you aware of how much overweight you are. This, in turn, will help you to cut out unnecessary calories you are consuming in the form or type of food which you are eating. This is very essential in a person having diabetes, as tailoring your diet as per your ideal body weight can bring down your blood sugar levels as well as weight by consuming lesser calories.
3] Socioeconomic conditions-
Diabetes was once known to be a disease of the rich and affluent people. This is partly true because this class of people is either too busy or simply lazy to do some exercise and indulge themselves in erratic eating habits.
As against this, the poor class of people does not have enough food for consumption and are mostly malnourished. This, in the long term, causes the liver to release more sugar into the blood by breaking down the fats stored as glycogen, which was formed as a result of the conversion of excess glucose absorbed from the intestines. This is also termed starvation diabetes.
4] Type of food one eats: –
In one of my earlier blogs, I had mentioned a Food Pyramid-this shows what a normal person should eat the most and what to eat the least. The same rule applies to a diabetic too, but with a cap on calories to be consumed.
Anyone with diabetes must focus on getting more fiber in his or her diet. This way you get complex carbohydrates and less of simple carbs (as in the product shown below)
How much calories you need daily: –
Diet in diabetes requires careful planning and includesbyour calory requirement, your physical activity and how much energy is spent in those activities.
To calculate the calories you need daily, you should know your Basal Metabolic Rate- BMR.
BMR is the minimum energy required by our body for carrying out involuntary functions such as breathing, pumping of blood by the heart, etc., while we are resting.
- Men: – 10 x weight in kg + 6.25 x height in cm – 5 x age in years +5
- Women: – 10 x weight in kg + 6.25 x height in cm – 5 x age in years – 161.
You can also use this BMR calculator for calculating your requirements-
BMR, Physical Activity and Required Calories: –
Now, go ahead, calculate your BMR and multiply it with the factor shown above to know how many calories you require per day to maintain your ideal body weight.
BMI based Calorie Requirement:
Another easy way to decide the approximate calories required by an adult individual of different categories is by following this simple calculation: –
- Normal BMI, active individuals- 22-25 Kcal/kg
- Normal BMI, sedentary individuals-30 Kcal/kg
- Thin/very active individuals-40 Kcal/kg
- Obese less active, sedentary individuals-20 Kcal/kg.
You can now multiply your weight to the calories required depending on which type of individual you fit in and then decide your diet accordingly.
Here is an interesting video to help you know what to eat in diabetes.
In my next article-
We now conclude Part 1 of diet in diabetes.
In my next article, I will be writing on-
- Different parameters of diet like the glycemic index,
- The total number of calories each food item has and,
- The importance of both in the treatment of diabetes.
Diet Control in Diabetics is the first steppingstone to Successful Blood Sugar Control, second is Regular Exercise and Third- Medicines. Click To Tweet



![ORAL ANTI-DIABETIC DRUGS[ OADS] 12 Diabetes logo](https://raodoctor.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/Untitled-design-2.png)