Table of Contents
Managing Anemia through Diet and Nutrition
In my recently concluded article, I had described different types of anemia. Here is a brief recap of the same-
Anemia (Doc) by K P Vasudeva RaoThe treatment of anemia depends upon the type and its root cause. In this article, we will learn various ways to take care of this condition.
Diet plays a crucial role in managing anemia, as certain nutrients are essential for red blood cell production and overall health.

Here are some dietary changes and nutritional strategies that can help manage anemia:
Incorporating Iron-rich Foods for anemia
One of the most effective ways to manage iron-deficiency anemia is by incorporating iron-rich foods into your diet. Iron is essential for the production of hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. Good dietary sources of iron include lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, tofu, spinach, kale, broccoli, and fortified cereals.
To manage iron-deficiency anemia, it is crucial to increase iron intake through dietary sources such as lean meats, beans, leafy green vegetables, and fortified cereals.
Your healthcare professionals may also prescribe iron supplements. Additionally, consuming vitamin C-rich foods alongside iron-rich foods can enhance iron absorption.
To enhance iron absorption, it is beneficial to consume foods rich in vitamin C alongside iron-rich foods. Citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and tomatoes are excellent sources of vitamin C. Avoid consuming iron-rich foods with calcium-rich foods or beverages, as calcium can inhibit iron absorption.
Including Vitamin B12-rich Foods
For individuals with this disorder, increasing intake of foods rich in vitamin B12 is crucial.
Managing vitamin B12 deficiency anemia involves increasing vitamin B12 intake through dietary sources such as meat, fish, dairy products, and fortified cereals. In some cases, vitamin B12 injections or supplements may be necessary to ensure adequate levels in the body.
Dr. K. P. V. Rao’s Health Blogs
Treating vitamin B12 deficiency anemia is like filling a car with gasoline when it’s running low. You need to increase your vitamin B12 intake through foods like meat, fish, dairy products, and fortified cereals, just like you need to refuel your car. In some cases, vitamin B12 injections or supplements are needed, similar to adding extra fuel to ensure the car has enough to keep running smoothly.
Good dietary sources of vitamin B12 include meat, fish, poultry, eggs, dairy products, and fortified cereals. Vegan individuals may need to consider vitamin B12 supplements or fortified plant-based alternatives.
In addition to dietary changes, it is important to address the underlying cause of vitamin B12 deficiency. This may involve treating conditions such as pernicious anemia or gastrointestinal disorders that affect the absorption of vitamin B12. Regular monitoring of vitamin B12 levels and follow-up with healthcare professionals is essential to ensure adequate treatment and prevent further complications.
Ensuring Sufficient Folic Acid Intake
Managing folic acid deficiency anemia involves increasing folic acid intake through dietary sources such as green leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, beans, and fortified grains. Folic acid supplements may be prescribed by a healthcare professional, especially for pregnant women or individuals with severe deficiencies.
To manage folic acid deficiency anemia, ensure sufficient intake of folic acid through these dietary sources:
- Green leafy vegetables: Spinach and kale are excellent sources of folic acid.
- Citrus fruits: Oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are rich in folic acid.
- Beans and lentils: These legumes are good sources of folic acid.
- Fortified grains: Look for cereals, bread, and pasta fortified with folic acid.
Use cooking methods like steaming or microwaving to preserve the folic acid content in these foods.
A Balanced and Nutrient-dense Diet
Aside from specific nutrients, maintaining a balanced and nutrient-dense diet is essential for managing anemia and supporting overall health.
Focus on consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. .
Limit your intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and alcoholic beverages, as they can impede nutrient absorption and contribute to the development of anemia.
The recommended daily intake of iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12 per kg body weight is not a common metric. However, the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and National Institute of Nutrition (NIN) have published an updated Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) and Estimated Average Requirements (EAR) for the Indian population. [Have a look at the table below]
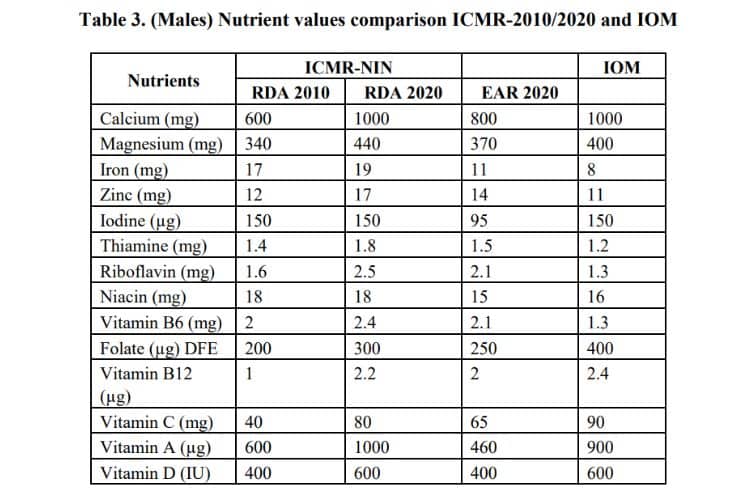
The summary of this recommendation is given below:
- Iron: The recommended daily intake of iron varies by age and gender. For adult men and women over 50 years, the recommended daily intake is 8 milligrams (mg). For women between the ages of 19 and 50, the recommended daily intake is 18 mg.
- Folic acid: The recommended daily intake of folic acid is 400 micrograms (mcg) for most adults.
- Vitamin B12: The recommended daily intake of vitamin B12 is 2.4 mcg for most adults.
It is important to note that the daily requirements for these nutrients may vary depending on individual health conditions and other factors such as pregnancy in women, malnutrition, chronic illnesse like Chronic Kidney Disease, etc. If you are concerned about your nutrient intake, it is best to consult with your doctor.
Supplements and Medical Advice
In some cases, dietary changes alone may not be sufficient to manage anemia, and supplements may be necessary. These supplements are avaiable as both syrups and capsules. [See the Image Below of what I usually prescribe to my patients- you can click the links to purchase them on Amazon Pharmacy]
However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplements, as excessive intake of certain nutrients can have adverse effects.
Supplements such as iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid may be recommended by a healthcare professional to address specific deficiencies. Monitoring your iron levels regularly by caring out iron level studies and adjusting your supplement dosage accordingly is crucial for effective management of anemia.
Disclosure: Some of the links used in this article are affiliate links. i.e., if you make a purchase, I will get a commission, at no extra cost to you. Please be rest assured that I only recommend products I genuinely believe in, and trust to be good for you too.
Additionally, seeking medical advice is essential to identify the underlying cause of the anemia and to develop an individualized treatment plan. Follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider will help track your progress and ensure that your treatment approach is appropriate and effective.
A healthcare professional can guide you on the appropriate dosage and duration of supplements based on your specific needs.
Additionally, it is crucial to follow your healthcare professional’s advice and treatment plan for managing anemia. Regular check-ups, blood tests, and monitoring of symptoms are essential to track progress and make any necessary adjustments to your management approach.
Medical Treatments for Anemia
In addition to dietary changes and supplements, medical treatments may be necessary to effectively manage anemia, especially in cases where the underlying cause requires intervention. Here are some common medical treatments for anemia:
Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions involve receiving healthy blood from a compatible donor to replace the deficient or abnormal red blood cells. This can provide immediate relief from anemia symptoms and can be life-saving in certain cases, such as severe hemolytic anemia or sickle cell crisis.
Medications
In some types of anemia, medications other than supplements, may be prescribed to address the underlying cause or manage symptoms. I also recommend deworming to take care of worm infestation.
The management of sickle cell anemia involves a multidisciplinary approach, including pain management, preventive medications such as antibiotics and hydroxyurea, blood transfusions, and possibly bone marrow transplantation in severe cases. Regular check-ups and genetic counseling are also essential for individuals with sickle cell anemia.
For example, individuals with sickle cell anemia may benefit from pain medications during sickle cell crises or preventive medications such as hydroxyurea to reduce the frequency and severity of crises. Immunosuppressive medications may be used in certain cases of hemolytic anemia caused by autoimmune disorders.
Surgical Interventions
The treatment for hemolytic anemia depends on the underlying cause and may involve medications to suppress the immune system, blood transfusions, or surgical removal of the spleen. In some cases, treating the underlying cause can resolve anemia.
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to manage anemia. For instance, individuals with severe hemolytic anemia may require a splenectomy, which involves surgical removal of the spleen to reduce the destruction of red blood cells.
Splenectomy is generally reserved for those with warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia. In this, the most common of the hemolytic anemias, antibodies are made against red blood cells, making them appear abnormal to the spleen. The spleen then clears them from the blood and destroys them.
Lifespan.org
Bone marrow transplantation may be considered in severe cases of sickle cell anemia or other inherited forms of anemia.
It is important to note that medical treatments for anemia should be prescribed and supervised by healthcare professionals. They will consider the underlying cause, individual health factors, and potential risks and benefits before recommending any specific treatments.
Conclusion
Remember, managing anemia requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses both lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Consult with healthcare professionals, including doctors and registered dietitians, to develop a personalized plan that addresses your specific needs and ensures the best possible outcomes.
Don’t let anemia drain your energy and affect your quality of life. With knowledge, proactive management, and support from healthcare professionals, you can regain strength and vitality. Take control of your health, embrace a balanced diet, and explore the available treatment options. Together, we can conquer anemia and live life to the fullest.
Final Words
I hope you have benefited by reading this article. If yes, do share it with others. Alternately, you can Click to Tweet here-
Understanding Anemia-Part 2-Learn how to manage it Share on XMy next topic for discussion will be about some Essential Minerals that our body needs to keep us healthy. Till then-
Adios.