Table of Contents
Interpreting abnormal results in hematology tests
While understanding the normal range for hematological parameters is crucial, interpreting abnormal results is equally important.
In my previous article, Decoding Hematology-Part 1, I discussed the normal parameters of various components of complete blood count.
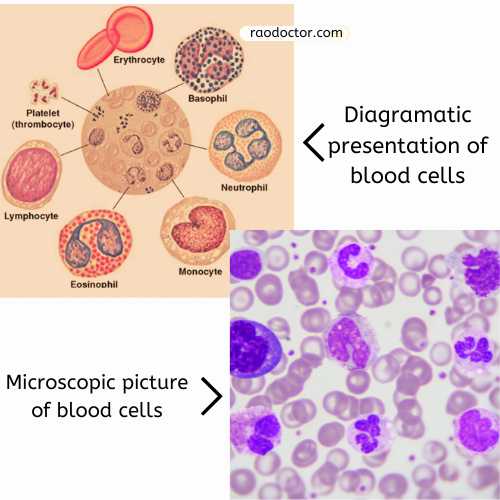
Continuing from where we left, in this article, we will learn about abnormal findings in hematology tests and their significance.
Abnormalities in red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelet parameters can indicate various health conditions and require further investigation.
How does an abnormal blood test look like?
In my last article I had put up a picture of a normal complete blood count. Now, have a look at this image below- it reveals a load of abnormal findings that we are going to discuss below in the paragraphs following this image-

The above image is of a patient having fever. It reveals-
- A low RBC counts
- Low hemoglobin level
- Low PCV
- Very high WBC count
- Very high Neutrophil level
- Very high Lymphocyte count
- Low platelet count and high platelet distribution width [PDW]
This report shows that the patient is suffering from either a viral disease like dengue or influenza.
The normal values I had discussed in my previous article. If you are not sure what the normal values should be, you can read it here-
Common abnormalities in RBC parameters and their significance
Abnormalities in red blood cell parameters can provide insights into conditions such as anemia, polycythemia, or bone marrow disorders.
A low red blood cell count (anemia) may indicate iron deficiency, vitamin B12 deficiency, or chronic disease.
Conversely, a high red blood cell count (polycythemia) may suggest dehydration, chronic lung disease, or certain types of cancer.
*Polycythemia is a condition where your blood has too many red blood cells, which makes it thicker and harder to flow. It can cause symptoms like-
- fatigue,
- itching,
- bruising, and
- bleeding problems.
It can also increase your risk of blood clots, headaches, stroke, heart attack, and other complications.
There are different types of polycythemias, and the treatment depends on the cause. Some common treatments are removing some blood (phlebotomy), taking medications to lower the red blood cell production or prevent clotting, and avoiding smoking and dehydration.
Useful Article- What is Polycythemia?
Other red blood cell parameters, such as MCV, MCH, and MCHC, can help further narrow down the underlying cause of abnormal findings.
For example, a low MCV may indicate iron deficiency anemia, while a high MCV may suggest vitamin B12 deficiency or folic acid deficiency anemia.
Common abnormalities in WBC parameters and their significance
Abnormalities in white blood cell parameters can indicate infections, immune disorders, or bone marrow disorders.
An increased white blood cell count (leukocytosis) may be a sign of
- infection,
- inflammation anywhere in the body, or
- leukemia [blood cancer].
Useful article- High Neutrophil Levels
On the other hand, a decreased white blood cell count (leukopenia) may indicate
- bone marrow disorders or
- immune system deficiencies and
- in some diseases like typhoid fever also the WBC count is low.
Different distributions of white blood cell types can also provide valuable information as mentioned below-
- An increased neutrophil count (neutrophilia) may indicate bacterial infections, such as pneumonia.
- An increased lymphocyte count (lymphocytosis) may suggest viral infections or certain types of leukemia.
- An increased eosinophil count suggests eosinophilia, an allergic response to pollen and dust. etc. This condition is commonly found in bronchial asthma or eosinophilic bronchitis.
Useful article- Causes of high white blood cell count.
Common abnormalities in platelet parameters and their significance
Platelets are a component of the blood clotting system that helps in stopping bleeding by helping form a clot.
Abnormal platelet parameters can indicate-
- bleeding disorders,
- bone marrow disorders, or
- certain medications’ side effects.
- a low platelet count (thrombocytopenia) may cause excessive bleeding, while
- a high platelet count (thrombocytosis) can lead to abnormal blood clotting.
The mean platelet volume (MPV) can help identify the size of platelets, with high values indicating larger platelets.
This can be relevant in diagnosing conditions such as immune thrombocytopenic purpura or myeloproliferative disorders.
Early disease detection through abnormal hematological test results
Detecting abnormalities in hematological tests can play a crucial role in the early detection of various diseases. Abnormal results can serve as red flags, prompting further investigations and interventions.
For example, abnormal red blood cell parameters may lead to the diagnosis of
- anemia, which can be caused by underlying conditions such as
- iron deficiency,
- vitamin B12 deficiency, or
- chronic diseases.
Early detection and treatment of these conditions can prevent complications and improve overall health outcomes.
Similarly, abnormal white blood cell parameters may indicate
- an ongoing infection,
- immune system disorders, or
- even leukemia.
Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help manage these conditions effectively.
Hematology tests can also aid in the early detection of blood cancers, such as leukemia.
Abnormalities in white blood cell parameters, such as an increased total count or abnormal distribution, may warrant further investigations, such as bone marrow biopsies or genetic testing.
Hematology tests for specific diseases (e.g., anemia, leukemia)
Hematology tests are instrumental in diagnosing and monitoring specific diseases.
For example, in the case of anemia, additional tests, such as
- iron studies,
- vitamin B12, and
- folate levels, can help identify the underlying cause.
This information is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment approach, whether it involves iron supplements, vitamin B12 injections, or other interventions.
In the case of leukemia, specific tests, such as flow cytometry or cytogenetic analysis, can provide detailed information about the type and characteristics of the cancer cells. This information helps guide treatment decisions, such as chemotherapy regimens or stem cell transplantation.
Importance of regular hematological testing for disease prevention
Regular hematological testing is essential for disease prevention and early detection. Routine blood tests can help identify potential health issues before they manifest with noticeable symptoms.
By detecting abnormalities in hematological parameters, healthcare professionals or your doctor can intervene early, leading to better health outcomes and improved quality of life.
Additionally, regular hematological testing is crucial for individuals with pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, as these conditions can have an impact on blood cell counts and function.
Monitoring hematological parameters regularly can help healthcare providers manage these conditions more effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding normal hematological test values and detecting abnormalities is vital for early disease detection.
Hematology tests, such as the Complete Blood Count, provide valuable insights into a person’s overall health and can help diagnose and monitor various diseases.
By interpreting abnormal results and taking appropriate actions, your healthcare professional/doctor can improve your health outcomes and enhance disease prevention efforts.
So, the next time you undergo a blood test, remember that your blood holds a treasure trove of information about your health!
Useful Resource:
- Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) Blood Test (verywellhealth.com)
- White Blood Cell Abnormality- Leukemia
Final Words
I hope you have understood the causes of abnormal hematology tests. If yes, please share this article on your social media circles by clicking the icons at the bottom of this article. Alternately, you can click to Tweet-
Decoding Hematology-Part 2 Share on XMy next article will be on an eye affliction that is happening commonly these days in elderly people- Retinal Detachment.
Do subscribe to my blogs by submitting the form provided in this article.

